Intramembranous solute and water fluxes during high intramembranous absorption rates in fetal sheep with and without lung liquid diversion
- PMID: 19398093
- PMCID: PMC2954255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.02.018
Intramembranous solute and water fluxes during high intramembranous absorption rates in fetal sheep with and without lung liquid diversion
Abstract
Objective: To examine mechanisms that mediate increased intramembranous solute and water absorption.
Study design: Intramembranous solute and water fluxes were measured in fetal sheep under basal conditions and after intraamniotic infusion of lactated Ringer's solution of 4 L/d for 3 days with and without lung liquid diversion.
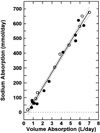
Results: Intramembranous sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, glucose, and lactate fluxes increased 2.5- to 7.9-fold, were linearly related to volume fluxes (r = 0.83-0.99), and were unaffected by lung liquid. All clearance rates, except that of lactate, increased to equal the intramembranous volume absorption rate during infusion.
Conclusion: Under basal conditions, passive diffusion makes a minor and bulk flow a major contribution to intramembranous solute absorption. During high absorption rates, the increase in solute absorption above basal levels appears to be due entirely to bulk flow and is unaffected by lung liquid. The increased bulk flow is consistent with vesicular transcytosis.
Figures
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

