Sgt1 dimerization is negatively regulated by protein kinase CK2-mediated phosphorylation at Ser361
- PMID: 19398558
- PMCID: PMC2707205
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.012732
Sgt1 dimerization is negatively regulated by protein kinase CK2-mediated phosphorylation at Ser361
Abstract
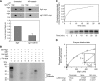
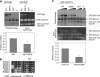
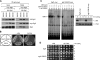
The kinetochore, which consists of centromere DNA and structural proteins, is essential for proper chromosome segregation in eukaryotes. In budding yeast, Sgt1 and Hsp90 are required for the binding of Skp1 to Ctf13 (a component of the core kinetochore complex CBF3) and therefore for the assembly of CBF3. We have previously shown that Sgt1 dimerization is important for this kinetochore assembly mechanism. In this study, we report that protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates Ser(361) on Sgt1, and this phosphorylation inhibits Sgt1 dimerization.
Figures
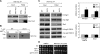
Similar articles
-
Sgt1 associates with Hsp90: an initial step of assembly of the core kinetochore complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(18):8069-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8069-8079.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15340069 Free PMC article.
-
Sgt1 dimerization is required for yeast kinetochore assembly.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3586-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806281200. Epub 2008 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19073600 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structure of the Sgt1-Skp1 complex: the link between Hsp90 and both SCF E3 ubiquitin ligases and kinetochores.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 31;7:41626. doi: 10.1038/srep41626. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28139700 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional coupling of Hsp90- and Sgt1-centred multi-protein complexes.EMBO J. 2008 Oct 22;27(20):2789-98. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.190. Epub 2008 Sep 25. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18818696 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinetochore.FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 24;389(1):70-4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00563-7. FEBS Lett. 1996. PMID: 8682209 Review.
Cited by
-
Origin of a folded repeat protein from an intrinsically disordered ancestor.Elife. 2016 Sep 13;5:e16761. doi: 10.7554/eLife.16761. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27623012 Free PMC article.
-
Plk1 phosphorylates Sgt1 at the kinetochores to promote timely kinetochore-microtubule attachment.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(19):4053-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00516-12. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22869522 Free PMC article.
-
Low-resolution structure of the full-length barley (Hordeum vulgare) SGT1 protein in solution, obtained using small-angle X-ray scattering.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 8;9(4):e93313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093313. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24714665 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative approaches to Hsp90 modulation for the treatment of cancer.Future Med Chem. 2014 Sep;6(14):1587-605. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.89. Future Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25367392 Free PMC article.
-
BUB3 that dissociates from BUB1 activates caspase-independent mitotic death (CIMD).Cell Death Differ. 2010 Jun;17(6):1011-24. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.207. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 20057499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheeseman I. M., Desai A. (2008) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 33–46 - PubMed
-
- Westermann S., Drubin D. G., Barnes G. (2007) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 563–571 - PubMed
-
- Sudakin V., Yen T. J. (2007) Biodrugs 21, 225–233 - PubMed
-
- Weaver B. A., Silk A. D., Montagna C., Verdier-Pinard P., Cleveland D. W. (2007) Cancer Cell 11, 25–36 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. (1982) Cell 29, 235–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

