Intracellular calcium strongly potentiates agonist-activated TRPC5 channels
- PMID: 19398778
- PMCID: PMC2712973
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200810153
Intracellular calcium strongly potentiates agonist-activated TRPC5 channels
Abstract
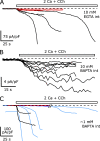
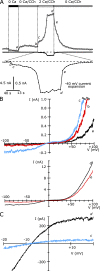
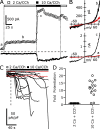
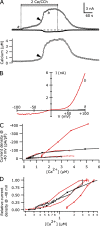
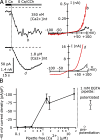
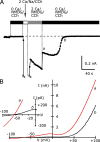
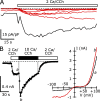
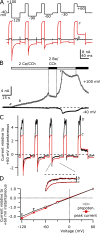
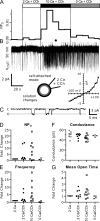
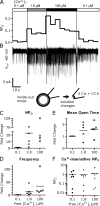
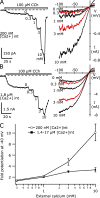
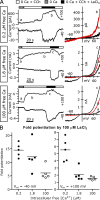
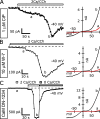
TRPC5 is a calcium (Ca(2+))-permeable nonselective cation channel expressed in several brain regions, including the hippocampus, cerebellum, and amygdala. Although TRPC5 is activated by receptors coupled to phospholipase C, the precise signaling pathway and modulatory signals remain poorly defined. We find that during continuous agonist activation, heterologously expressed TRPC5 currents are potentiated in a voltage-dependent manner ( approximately 5-fold at positive potentials and approximately 25-fold at negative potentials). The reversal potential, doubly rectifying current-voltage relation, and permeability to large cations such as N-methyl-d-glucamine remain unchanged during this potentiation. The TRPC5 current potentiation depends on extracellular Ca(2+): replacement by Ba(2+) or Mg(2+) abolishes it, whereas the addition of 10 mM Ca(2+) accelerates it. The site of action for Ca(2+) is intracellular, as simultaneous fura-2 imaging and patch clamp recordings indicate that potentiation is triggered at approximately 1 microM [Ca(2+)]. This potentiation is prevented when intracellular Ca(2+) is tightly buffered, but it is promoted when recording with internal solutions containing elevated [Ca(2+)]. In cell-attached and excised inside-out single-channel recordings, increases in internal [Ca(2+)] led to an approximately 10-20-fold increase in channel open probability, whereas single-channel conductance was unchanged. Ca(2+)-dependent potentiation should result in TRPC5 channel activation preferentially during periods of repetitive firing or coincident neurotransmitter receptor activation.
Figures

References
-
- Bezzerides V.J., Ramsey I.S., Kotecha S., Greka A., Clapham D.E. 2004. Rapid vesicular translocation and insertion of TRP channels.Nat. Cell Biol. 6:709–720 - PubMed
-
- Biddlecome G.H., Berstein G., Ross E.M. 1996. Regulation of phospholipase C-beta1 by Gq and m1 muscarinic cholinergic receptor. Steady-state balance of receptor-mediated activation and GTPase-activating protein-promoted deactivation.J. Biol. Chem. 271:7999–8007 - PubMed
-
- Chung M.K., Guler A.D., Caterina M.J. 2005. Biphasic currents evoked by chemical or thermal activation of the heat-gated ion channel, TRPV3.J. Biol. Chem. 280:15928–15941 - PubMed
-
- Chung M.K., Guler A.D., Caterina M.J. 2008. TRPV1 shows dynamic ionic selectivity during agonist stimulation.Nat. Neurosci. 11:555–564 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

