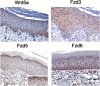
Wnt5a exhibits layer-specific expression in adult skin, is upregulated in psoriasis, and synergizes with type 1 interferon
- PMID: 19399181
- PMCID: PMC2670517
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005354
Wnt5a exhibits layer-specific expression in adult skin, is upregulated in psoriasis, and synergizes with type 1 interferon
Abstract
Background: Wnt5a is a member of the wingless-type patterning regulators important in pre-natal development. The expression and distribution of Wnt5a and its receptors frizzled (fzd) 3 and fzd 5 in adult human skin have not been comprehensively studied to date.
Methodology/principal findings: We here show that Wnt5a, fzd3, fzd5, as well as fzd6 are restricted to specific layers in normal epidermis, analogous to their zonal distribution in hair follicles, suggesting a role in adult skin differentiation. In line, Wnt5a and fzd5 are both overexpressed and re-distributed in the epidermis of psoriasis which involves disturbed keratinocyte differentiation. Functionally, Wnt5a lowers the concentration of IFN required to induce target genes, and increases the magnitude of IFN target gene induction, suggesting a molecular mechanism underlying IFN hypersensitivity in psoriasis. Finally, we identify nedd8 and the amyloid precursor APP, previously shown to be upregulated in psoriasis, as targets of synergistic IFNalpha/Wnt5a induction.
Conclusions/significance: The present data (i) suggest that Wnt5a regulates epidermal differentiation even in adult skin and (ii) identify synergistic induction of type 1 IFN target genes as a novel mode of Wnt5a action. Targeting Wnt5a in the skin may reduce IFN hypersensitivity and be of therapeutical value.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Wnt/β-Catenin and Wnt5a/Ca Pathways Regulate Proliferation and Apoptosis of Keratinocytes in Psoriasis Lesions.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):1890-902. doi: 10.1159/000430158. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26202350
-
Evidence for altered Wnt signaling in psoriatic skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2010 Jul;130(7):1849-59. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.67. Epub 2010 Apr 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20376066 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Wnt5a in mouse epidermis causes no psoriasis phenotype but an impairment of hair follicle anagen development.Exp Dermatol. 2014 Dec;23(12):926-8. doi: 10.1111/exd.12539. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25219536
-
Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in diseases.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Jan;204(1):17-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02294.x. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21518267 Review.
-
Insight into the role of Wnt5a-induced signaling in normal and cancer cells.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;314:117-48. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25619716 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Role and Therapeutic Implication of Wnt Signaling Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:9392132. doi: 10.1155/2016/9392132. Epub 2016 Mar 27. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27110577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitinating enzyme 4 facilitates chemoresistance in glioblastoma by inhibiting P53 activity.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jan;17(1):958-964. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9654. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30655854 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of APP and its metabolites outside the central nervous system.Exp Gerontol. 2013 Jul;48(7):608-11. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2012.07.009. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Exp Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 22846461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Wnt5a with Notch1 is Critical for the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis.Ann Dermatol. 2016 Feb;28(1):45-54. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.1.45. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Ann Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26848218 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a is strongly expressed at the leading edge in non-melanoma skin cancer, forming active gradients, while canonical Wnt signalling is repressed.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031827. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng CW, Yeh JC, Fan TP, Smith SK, Charnock-Jones DS. Wnt5a-mediated non-canonical Wnt signalling regulates human endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;365:285–290. - PubMed
-
- Yu JM, Jun ES, Jung JS, Suh SY, Han JY, et al. Role of Wnt5a in the proliferation of human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett 2007 - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki A, Torii K, Yamashita Y, Nishizawa K, Kanekura K, et al. Wnt5a promotes adhesion of human dermal fibroblasts by triggering a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signal. Cell Signal 2007 - PubMed
-
- Safholm A, Leandersson K, Dejmek J, Nielsen CK, Villoutreix BO, et al. A formylated hexapeptide ligand mimics the ability of Wnt-5a to impair migration of human breast epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:2740–2749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

