Patient-specific modeling of cardiovascular mechanics
- PMID: 19400706
- PMCID: PMC4581431
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160521
Patient-specific modeling of cardiovascular mechanics
Abstract
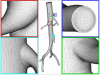
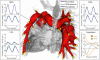
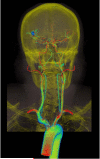
Advances in numerical methods and three-dimensional imaging techniques have enabled the quantification of cardiovascular mechanics in subject-specific anatomic and physiologic models. Patient-specific models are being used to guide cell culture and animal experiments and test hypotheses related to the role of biomechanical factors in vascular diseases. Furthermore, biomechanical models based on noninvasive medical imaging could provide invaluable data on the in vivo service environment where cardiovascular devices are employed and on the effect of the devices on physiologic function. Finally, patient-specific modeling has enabled an entirely new application of cardiovascular mechanics, namely predicting outcomes of alternate therapeutic interventions for individual patients. We review methods to create anatomic and physiologic models, obtain properties, assign boundary conditions, and solve the equations governing blood flow and vessel wall dynamics. Applications of patient-specific models of cardiovascular mechanics are presented, followed by a discussion of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Figures

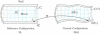



References
-
- Moore JA, Rutt BK, Karlik SJ, Yin K, Ethier CR. Computational Blood Flow Modeling Based on In Vivo Measurements. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 1999;27:627–40. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CA, Draney MT, Ku JP, Parker D, Steele BN, et al. Predictive medicine: computational techniques in therapeutic decision-making. Comput Aided Surg. 1999;4:231–47. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CA, Hughes TJR, Zarins CK. Finite Element Modeling of Blood Flow in Arteries. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. 1998;158:155–96.
-
- Long Q, Xu XY, Ariff B, Thom SA, Hughes AD, et al. Reconstruction of blood flow patterns in a human carotid bifurcation: a combined CFD and MRI study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;11:299–311. Stant. - PubMed
-
- Steinman DA. Image-based computational fluid dynamics modeling in realistic arterial geometries. Ann Biomed Eng. 2002;30:483–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

