Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage
- PMID: 19400724
- PMCID: PMC2768555
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage
Abstract
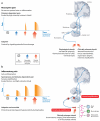
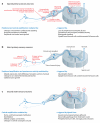
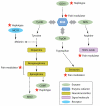
Neuropathic pain is triggered by lesions to the somatosensory nervous system that alter its structure and function so that pain occurs spontaneously and responses to noxious and innocuous stimuli are pathologically amplified. The pain is an expression of maladaptive plasticity within the nociceptive system, a series of changes that constitute a neural disease state. Multiple alterations distributed widely across the nervous system contribute to complex pain phenotypes. These alterations include ectopic generation of action potentials, facilitation and disinhibition of synaptic transmission, loss of synaptic connectivity and formation of new synaptic circuits, and neuroimmune interactions. Although neural lesions are necessary, they are not sufficient to generate neuropathic pain; genetic polymorphisms, gender, and age all influence the risk of developing persistent pain. Treatment needs to move from merely suppressing symptoms to a disease-modifying strategy aimed at both preventing maladaptive plasticity and reducing intrinsic risk.
Figures



References
-
- Abbadie C. Chemokines, chemokine receptors and pain. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:529–34. - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsen B, Zhao J, Asante CO, Cendan CM, Marsh S, et al. The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science. 2008;321:702–5. - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Birch R. Restoration of sensory function and lack of long-term chronic pain syndromes after brachial plexus injury in human neonates. Brain. 2002;125:113–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

