Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, OX40-ligand, and interleukin-25 in allergic responses
- PMID: 19400908
- PMCID: PMC2744577
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03241.x
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, OX40-ligand, and interleukin-25 in allergic responses
Abstract
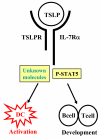
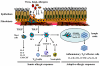
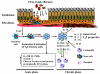
Allergic diseases are often triggered by environmental allergens that induce dominant type 2 immune responses, characterized by the infiltrated T-helper type 2 (TH2) lymphocytes, eosinophils, and elevated TH2 cytokines. In addition to TH2 type immune responses, epithelial stress and injury linked to tissue remodelling are often observed, suggesting that epithelial cells may play important role in regulating allergic responses. Dendritic cells (DCs), the professional antigen-presenting cells with the capabilities of sampling allergens, are considered as the key player on instructing TH2 immune responses. Whether inflamed epithelium can regulate innate immunity, such as macrophages and DCs, which in turn instructs adaptive immunity has long been hypothesized. Studies of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), an epithelial cells-derived cytokine, that can strongly activate DCs, provide important evidences that the epithelial barrier can trigger allergic diseases by regulating immune responses. The finding that OX40/OX40Ligand (OX40L) interactions are the molecular trigger responsible for the induction and maintenance of TH2 responses by TSLP-activated DCs provides a plausible molecular explanation for TSLP-mediated allergy. Recent progresses in characterizing the pro-inflammatory IL-17 cytokine family have added an additional layer of complexity on the regulation of allergic inflammation. TSLP-DCs can induce a robust expansion of TH2 memory cells and strengthen functional attributes by up-regulating their surface expression of IL-17RB (IL-25R), the receptor for cytokine IL-17E (IL-25), a distinct member of IL-17 cytokine family. IL-17E (also known as IL-25) produced by epithelial cells, and other innate cells, such as eosinphils, basophils, and mast cells, are shown to regulate adaptive immunity by enhancing TH2 cytokine productions. These exciting findings expand our knowledge of the complex immunological cascades that result in allergic inflammation and may provide novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of allergic diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: a promising therapeutic target for allergic diseases.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;160(1):18-26. doi: 10.1159/000341665. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22948028 Review.
-
IL-33 promotes the induction and maintenance of Th2 immune responses by enhancing the function of OX40 ligand.Allergol Int. 2014 Sep;63(3):443-55. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.13-OA-0672. Epub 2014 May 25. Allergol Int. 2014. PMID: 24851948
-
IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC-activated Th2 memory cells.J Exp Med. 2007 Aug 6;204(8):1837-47. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070406. Epub 2007 Jul 16. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17635955 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine H4 receptor regulates Th2-cytokine profile through thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic rhinitis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jun;276(6):1655-1661. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05369-w. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30848348
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of TSLP function in human allergic disorders--TSLP programs the "Th2 code" in dendritic cells.Allergol Int. 2012 Mar;61(1):35-43. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.11-RAI-0376. Epub 2011 Dec 25. Allergol Int. 2012. PMID: 22189594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cells and basophils are essential for allergies: mechanisms of allergic inflammation and a proposed procedure for diagnosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Oct;34(10):1270-83. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.88. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23974516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ncRNAs in Type-2 Immunity.Noncoding RNA. 2020 Mar 6;6(1):10. doi: 10.3390/ncrna6010010. Noncoding RNA. 2020. PMID: 32155783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic low dose chlorine exposure aggravates allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness and activates inflammasome pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e106861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106861. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25202911 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of TSLP in Atopic Dermatitis: From Pathogenetic Molecule to Therapeutical Target.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Apr 15;2023:7697699. doi: 10.1155/2023/7697699. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37096155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ILC2s and fungal allergy.Allergol Int. 2015 Jul;64(3):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 May 18. Allergol Int. 2015. PMID: 26117252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leonard WJ. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:200–8. - PubMed
-
- Friend SL, Hosier S, Nelson A, Foxworthe D, Williams DE, Farr A. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp Hematol. 1994;22:321–8. - PubMed
-
- Pandey A, Ozaki K, Baumann H, Levin SD, Puel A, Farr AG, Ziegler SF, Leonard WJ, Lodish HF. Cloning of a receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Park LS, Martin U, Garka K, Gliniak B, Di Santo JP, Muller W, Largaespada DA, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Farr AG, Ziegler SF, Morrissey PJ, Paxton R, Sims JE. Cloning of the murine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor: Formation of a functional heteromeric complex requires interleukin 7 receptor. J Exp Med. 2000;192:659–70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reche PA, Soumelis V, Gorman DM, Clifford T, Liu M, Travis M, Zurawski SM, Johnston J, Liu YJ, Spits H, de Waal MR, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:336–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

