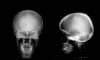
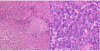
Treatment of multicentric Castleman's Disease accompanying multiple myeloma with bortezomib: a case report
- PMID: 19400935
- PMCID: PMC2686727
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-2-19
Treatment of multicentric Castleman's Disease accompanying multiple myeloma with bortezomib: a case report
Abstract
Multicentric Castleman's disease (MCD) is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder of unknown etiology and characterized by various clinical manifestations and multiple organ involvement. It has been reported in association with POEMS syndrome and can progress to Kaposi's sarcoma or malignant lymphoma. The disease runs a more aggressive course and a poor prognosis. Optimal therapies have not been well established up to now. We here reported a case of rare MCD complicated with multiple myeloma who received bortezomib and achieved very good remission. To our knowledge, this is the first report on MCD in the setting of multiple myeloma with good response to bortezomib.
Figures
References
-
- Gaba AR, Stein RS, Sweet DL, Variakojis D. Multicentric giant lymph node hyperplasia. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1978;69:86–90. - PubMed
-
- Yoshizaki K, Matsuda T, Nishimoto N, Kuritani T, Taeho L, Aozasa K, Nakahata T, Kawai H, Tagoh H, Komori T. Pathogenic significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2) in Castleman's disease. Blood. 1989;74:1360–1367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical