The effect of age on insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in first-degree relatives of type 1 diabetic patients: a population analysis
- PMID: 19401372
- PMCID: PMC2708949
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2008-2687
The effect of age on insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in first-degree relatives of type 1 diabetic patients: a population analysis
Abstract
Context: Understanding the role of insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes may lead to new prevention strategies. Estimates of insulin resistance in first-degree relatives of those with type 1 diabetes may be obtained using the minimal model of glucose kinetics incorporating a population approach.
Objective: The objective of the study was to explore parameters contributing to glucose homeostasis in a cross-sectional study of first-degree relatives across a wide age range.
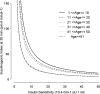
Design: Insulin sensitivity (SI) was assessed using the minimal model of glucose kinetics after an oral glucose tolerance test combined with nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. Beta-cell function was measured from the insulinogenic index at 30 min (IGI(30)). Disposition index (DI) was estimated as the product of SI and IGI(30).
Setting: The study was conducted at an academic center.
Subjects: Subjects included 1241 first-degree relatives (aged 2-75 yr).
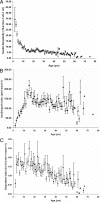
Results: SI was found to be negatively correlated with age, whereas IGI(30) increased until young adulthood. The increase IGI(30) was apparently insufficient to compensate for the insulin resistance because DI decreased linearly at the rate of 0.035 (10(-2) min(-1) mmol(-1) liter per year) after young adulthood. Both IGI(30) and DI were significantly lower in those with vs. without autoantibodies, whereas there was no difference between these groups with respect to SI.
Conclusions: Beta-cell function, adjusted for age-related insulin resistance, decreases throughout life in first-degree relatives. This deterioration may be exacerbated in the presence of autoantibodies. Oral glucose tolerance test data combined with a nonlinear mixed-effect modeling population approach may be a useful technique to evaluate SI and secretion in a population.
Figures

References
-
- Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Koczwara K, Ziegler AG 2005 Natural history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 54(Suppl 2):S25–S31 - PubMed
-
- Haller MJ, Atkinson MA, Schatz D 2005 Type 1 diabetes mellitus: etiology, presentation, and management. Pediatr Clin North Am 52:1553–1578 - PubMed
-
- Kimpimäki T, Kulmala P, Savola K, Vähäsalo P, Reijonen H, Ilonen J, Akerblom HK, Knip M 2000 Disease-associated autoantibodies as surrogate markers of type 1 diabetes in young children at increased genetic risk. Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:1126–1132 - PubMed
-
- Eisenbarth GS, Gianani R, Yu L, Pietropaolo M, Verge CF, Chase HP, Redondo MJ, Colman P, Harrison L, Jackson R 1998 Dual-parameter model for prediction of type I diabetes mellitus. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 110:126–135 - PubMed
-
- Bingley PJ, Christie MR, Bonifacio E, Bonfanti R, Shattock M, Fonte M, Bottazzo GF, Gale EA 1994 Combined analysis of autoantibodies improves prediction of IDDM in islet cell antibody positive relatives. Diabetes 43:1304–1310 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

