The presence and severity of chronic kidney disease predicts all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 19401416
- PMCID: PMC2699848
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1543
The presence and severity of chronic kidney disease predicts all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to identify clinical features associated with premature mortality in a large contemporary cohort of adults with type 1 diabetes.
Research design and methods: The Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy (FinnDiane) study is a national multicenter prospective follow-up study of 4,201 adults with type 1 diabetes from 21 university and central hospitals, 33 district hospitals, and 26 primary health care centers across Finland.
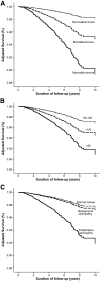
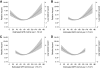
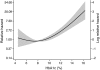
Results: During a median 7 years of follow-up, there were 291 deaths (7%), 3.6-fold (95% CI 3.2-4.0) more than that observed in the age- and sex-matched general population. Excess mortality was only observed in individuals with chronic kidney disease. Individuals with normoalbuminuria showed no excess mortality beyond the general population (standardized mortality ratio [SMR] 0.8, 95% CI 0.5-1.1), independent of the duration of diabetes. The presence of microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, and end-stage kidney disease was associated with 2.8, 9.2, and 18.3 times higher SMR, respectively. The increase in mortality across each stage of albuminuria was equivalent to the risk conferred by preexisting macrovascular disease. In addition, the glomerular filtration rate was independently associated with mortality, such that individuals with impaired kidney function, as well as those demonstrating hyperfiltration, had an increased risk of death.
Conclusions: An independent graded association was observed between the presence and severity of kidney disease and mortality in a large contemporary cohort of individuals with type 1 diabetes. These findings highlight the clinical and public health importance of chronic kidney disease and its prevention in the management of type 1 diabetes.
Figures
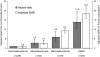
References
-
- Hovind P, Tarnow L, Rossing K, Rossing P, Eising S, Larsen N, Binder C, Parving HH: Decreasing incidence of severe diabetic microangiopathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1258– 1264 - PubMed
-
- Messent JW, Elliott TG, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Keen H, Viberti GC: Prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a twenty-three year follow-up study. Kidney Int 1992; 41: 836– 839 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

