Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects beta-cells against apoptosis by increasing the activity of an IGF-2/IGF-1 receptor autocrine loop
- PMID: 19401425
- PMCID: PMC2712796
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0063
Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects beta-cells against apoptosis by increasing the activity of an IGF-2/IGF-1 receptor autocrine loop
Abstract
Objective: The gluco-incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) protect beta-cells against cytokine-induced apoptosis. Their action is initiated by binding to specific receptors that activate the cAMP signaling pathway, but the downstream events are not fully elucidated. Here we searched for mechanisms that may underlie this protective effect.
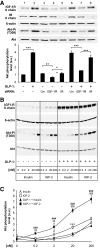
Research design and methods: We performed comparative transcriptomic analysis of islets from control and GipR(-/-);Glp-1-R(-/-) mice, which have increased sensitivity to cytokine-induced apoptosis. We found that IGF-1 receptor expression was markedly reduced in the mutant islets. Because the IGF-1 receptor signaling pathway is known for its antiapoptotic effect, we explored the relationship between gluco-incretin action, IGF-1 receptor expression and signaling, and apoptosis.
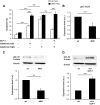
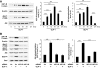
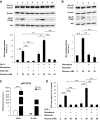
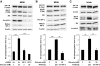
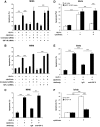
Results: We found that GLP-1 robustly stimulated IGF-1 receptor expression and Akt phosphorylation and that increased Akt phosphorylation was dependent on IGF-1 but not insulin receptor expression. We demonstrated that GLP-1-induced Akt phosphorylation required active secretion, indicating the presence of an autocrine activation mechanism; we showed that activation of IGF-1 receptor signaling was dependent on the secretion of IGF-2. We demonstrated, both in MIN6 cell line and primary beta-cells, that reducing IGF-1 receptor or IGF-2 expression or neutralizing secreted IGF-2 suppressed GLP-1-induced protection against apoptosis.
Conclusions: An IGF-2/IGF-1 receptor autocrine loop operates in beta-cells. GLP-1 increases its activity by augmenting IGF-1 receptor expression and by stimulating secretion; this mechanism is required for GLP-1-induced protection against apoptosis. These findings may lead to novel ways of preventing beta-cell loss in the pathogenesis of diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GLP-1 protects β-cells against apoptosis by enhancing the activity of an IGF-2/IGF1-receptor autocrine loop.Islets. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):280-2. doi: 10.4161/isl.1.3.9932. Islets. 2009. PMID: 21099285
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 increases beta-cell glucose competence and proliferation by translational induction of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 2;285(14):10538-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.091116. Epub 2010 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20145256 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Regulates Cholecystokinin Production in β-Cells to Protect From Apoptosis.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jul;29(7):978-87. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1030. Epub 2015 May 18. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25984632 Free PMC article.
-
Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and β cell preservation.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;107(2):248-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21820006 Review.
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
Cited by
-
Gluco-incretins regulate beta-cell glucose competence by epigenetic silencing of Fxyd3 expression.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 24;9(7):e103277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103277. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25058609 Free PMC article.
-
Failure of the Brain Glucagon-Like Peptide-1-Mediated Control of Intestinal Redox Homeostasis in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 13;10(7):1118. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071118. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356351 Free PMC article.
-
Intravital imaging of islet Ca2+ dynamics reveals enhanced β cell connectivity after bariatric surgery in mice.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 27;12(1):5165. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25423-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34453049 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering genetic linkage between periodontitis and type 1 diabetes: A bioinformatics study.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 27;14:1147819. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1147819. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37051594 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of gastric bypass surgery on the incretins.Diabetes Metab. 2009 Dec;35(6 Pt 2):513-7. doi: 10.1016/S1262-3636(09)73458-5. Diabetes Metab. 2009. PMID: 20152736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouwens L, Rooman I: Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass. Physiol Rev 2005; 85: 1255– 1270 - PubMed
-
- Eizirik DL, Mandrup-Poulsen T: A choice of death: the signal-transduction of immune-mediated beta-cell apoptosis. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 2115– 2133 - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC: Beta-cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003; 52: 102– 110 - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab 2006; 3: 153– 165 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

