Exosite determinants of serpin specificity
- PMID: 19401470
- PMCID: PMC2742806
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R800064200
Exosite determinants of serpin specificity
Abstract
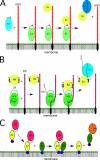
Serpins form an enormous superfamily of 40-60-kDa proteins found in almost all types of organisms, including humans. Most are one-use suicide substrate serine and cysteine proteinase inhibitors that have evolved to finely regulate complex proteolytic pathways, such as blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, and inflammation. Despite distinct functions for each serpin, there is much redundancy in the primary specificity-determining residues. However, many serpins exploit additional exosites to generate the exquisite specificity that makes a given serpin effective only when certain other criteria, such as the presence of specific cofactors, are met. With a focus on human serpins, this minireview examines use of exosites by nine serpins in the initial complex-forming phase to modulate primary specificity in either binary serpin-proteinase complexes or ternary complexes that additionally employ a protein or other cofactor. A frequent theme is down-regulation of inhibitory activity unless the exosite(s) are engaged. In addition, the use of exosites by maspin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 to indirectly affect proteolytic processes is considered.
Figures
References
-
- Gettins P. G. (2002) Chem. Rev. 102, 4751–4804 - PubMed
-
- Steenbakkers P. J., Irving J. A., Harhangi H. R., Swinkels W. J., Akhmanova A., Dijkerman R., Jetten M. S., van der Drift C., Whisstock J. C., op den Kamp H. J. (2008) Mycol. Res. 112, 999–1006 - PubMed
-
- Irving J. A., Pike R. N., Lesk A. M., Whisstock J. C. (2000) Genome Res. 10, 1845–1864 - PubMed
-
- Dementiev A., Dobó J., Gettins P. G. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 3452–3457 - PubMed
-
- Chuang Y. J., Swanson R., Raja S. M., Bock S. C., Olson S. T. (2001) Biochemistry 40, 6670–6679 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

