Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 expression inhibits urethane-induced pulmonary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice
- PMID: 19401523
- PMCID: PMC2697576
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0057
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 expression inhibits urethane-induced pulmonary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice
Abstract
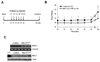
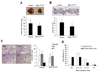
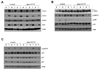
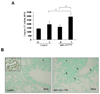
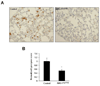
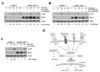
The expression of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 (NAG-1) inhibits gastrointestinal tumorigenesis in NAG-1 transgenic mice (C57/BL6 background). In the present study, we investigated whether the NAG-1 protein would alter urethane-induced pulmonary lesions in NAG-1 transgenic mice on an FVB background (NAG-1(Tg+/FVB)). NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice had both decreased number and size of urethane-induced tumors, compared with control littermates (NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) = 16 +/- 4 per mouse versus control = 20 +/- 7 per mouse, P < 0.05). Urethane-induced pulmonary adenomas and adenocarcinomas were observed in control mice; however, only pulmonary adenomas were observed in NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice. Urethane-induced tumors from control littermates and NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice highly expressed proteins in the arachidonic acid pathway (cyclooxygenases 1/2, prostaglandin E synthase, and prostaglandin E(2) receptor) and highly activated several kinases (phospho-Raf-1 and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2). However, only urethane-induced p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation was decreased in NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice. Furthermore, significantly increased apoptosis in tumors of NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice compared with control mice was observed as assessed by caspase-3/7 activity. In addition, fewer inflammatory cells were observed in the lung tissue isolated from urethane-treated NAG-1(Tg+/FVB) mice compared with control mice. These results paralleled in vitro assays using human A549 pulmonary carcinoma cells. Less phosphorylated p38 MAPK was observed in cells overexpressing NAG-1 compared with control cells. Overall, our study revealed for the first time that the NAG-1 protein inhibits urethane-induced tumor formation, probably mediated by the p38 MAPK pathway, and is a possible new target for lung cancer chemoprevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Nikitin AY, Alcaraz A, Anver MR, et al. Classification of proliferative pulmonary lesions of the mouse: recommendations of the mouse models of human cancers consortium. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2307–2316. - PubMed
-
- Schuller HM, Cekanova M. NNK-induced hamster lung adenocarcinomas over-express beta2-adrenergic and EGFR signaling pathways. Lung Cancer. 2005;49:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Bauer AK, Dwyer-Nield LD, Malkinson AM. High cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) contents in mouse lung tumors. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:543–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

