Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) are required for epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of the Akt-mTORC1 pathway
- PMID: 19401591
- PMCID: PMC4138699
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2000118
Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) are required for epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of the Akt-mTORC1 pathway
Erratum in
- Sci Signal. 2010;3(121):er2
Abstract
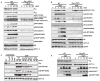
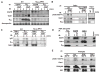
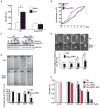
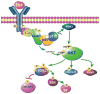
The precise mechanism whereby epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates the serine-threonine kinase Akt and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 (mTORC1) remains elusive. Here, we report that the alpha subunits of the heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) are critical for this activation process. Both Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) formed complexes with growth factor receptor binding 2 (Grb2)-associated binding protein 1 (Gab1) and the EGF receptor (EGFR) and were required for the phosphorylation of Gab1 and its subsequent interaction with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to EGF. Loss of Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) severely impaired the activation of Akt and of p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1, downstream targets of mTORC1, in response to EGF, heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor, and transforming growth factor alpha, but not insulin, insulin-like growth factor, or platelet-derived growth factor. In addition, ablation of Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) largely inhibited EGF-induced cell growth, migration, and survival and the accumulation of cyclin D1. Overall, this study suggests that Galpha(i1) and Galpha(i3) lie downstream of EGFR, but upstream of Gab1-mediated activation of Akt and mTORC1, thus revealing a role for Galpha(i) proteins in mediating EGFR signaling.
Figures



References
-
- Rozengurt E. Mitogenic signaling pathways induced by G protein-coupled receptors. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:589–602. - PubMed
-
- Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Whelan J, Bertrand FE, Ludwig DE, Bäsecke J, Libra M, Stivala F, Milella M, Tafuri A, Lunghi P, Bonati A, Martelli AM, McCubrey JA. Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways to leukemia. Leukemia. 2008;22:686–707. - PubMed
-
- Sabatini DM. mTOR and cancer: Insights into a complex relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:729–734. - PubMed
-
- Greer EL, Brunet A. FOXO transcription factors in ageing and cancer. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2008;192:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Lam EW, Francis RE, Petkovic M. FOXO transcription factors: Key regulators of cell fate. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:722–726. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

