Peptide Bbeta(15-42) preserves endothelial barrier function in shock
- PMID: 19401765
- PMCID: PMC2670535
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005391
Peptide Bbeta(15-42) preserves endothelial barrier function in shock
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2009;4(6) doi: 10.1371/annotation/9ae032a2-c48d-46d9-9f8f-d3f401714e42 doi: 10.1371/annotation/9ae032a2-c48d-46d9-9f8f-d3f401714e42
Abstract
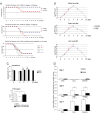
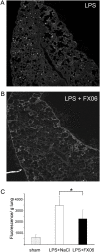
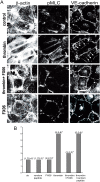
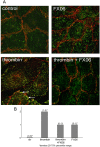
Loss of vascular barrier function causes leak of fluid and proteins into tissues, extensive leak leads to shock and death. Barriers are largely formed by endothelial cell-cell contacts built up by VE-cadherin and are under the control of RhoGTPases. Here we show that a natural plasmin digest product of fibrin, peptide Bbeta15-42 (also called FX06), significantly reduces vascular leak and mortality in animal models for Dengue shock syndrome. The ability of Bbeta15-42 to preserve endothelial barriers is confirmed in rats i.v.-injected with LPS. In endothelial cells, Bbeta15-42 prevents thrombin-induced stress fiber formation, myosin light chain phosphorylation and RhoA activation. The molecular key for the protective effect of Bbeta15-42 is the src kinase Fyn, which associates with VE-cadherin-containing junctions. Following exposure to Bbeta15-42 Fyn dissociates from VE-cadherin and associates with p190RhoGAP, a known antagonists of RhoA activation. The role of Fyn in transducing effects of Bbeta15-42 is confirmed in Fyn(-/-) mice, where the peptide is unable to reduce LPS-induced lung edema, whereas in wild type littermates the peptide significantly reduces leak. Our results demonstrate a novel function for Bbeta15-42. Formerly mainly considered as a degradation product occurring after fibrin inactivation, it has now to be considered as a signaling molecule. It stabilizes endothelial barriers and thus could be an attractive adjuvant in the treatment of shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Faust SN, Levin M, Harrison OB, Goldin RD, Lockhart MS, et al. Dysfunction of endothelial protein C activation in severe meningococcal sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:408–416. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda N, Hattori Y. Vascular biology in sepsis: pathophysiological and therapeutic significance of vascular dysfunction. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2007;43:117–137. - PubMed
-
- Petzelbauer P, Zacharowski PA, Miyazaki Y, Friedl P, Wickenhauser G, et al. The fibrin-derived peptide Bbeta15-42 protects the myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nat Med. 2005;11:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Sohn RH, Deming CB, Johns DC, Champion HC, Bian C, et al. Regulation of endothelial thrombomodulin expression by inflammatory cytokines is mediated by activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. Blood. 2005;105:3910–3917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

