Intrahepatic bile ducts develop according to a new mode of tubulogenesis regulated by the transcription factor SOX9
- PMID: 19403103
- PMCID: PMC2743481
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.02.051
Intrahepatic bile ducts develop according to a new mode of tubulogenesis regulated by the transcription factor SOX9
Abstract
Background & aims: A number of diseases are characterized by defective formation of the intrahepatic bile ducts. In the embryo, hepatoblasts differentiate to cholangiocytes, which give rise to the bile ducts. Here, we investigated duct development in mouse liver and characterized the role of the SRY-related HMG box transcription factor 9 (SOX9).
Methods: We identified SOX9 as a new biliary marker and used it in immunostaining experiments to characterize bile duct morphogenesis. The expression of growth factors was determined by in situ hybridization and immunostaining, and their role was studied on cultured hepatoblasts. SOX9 function was investigated by phenotyping mice with a liver-specific inactivation of Sox9.
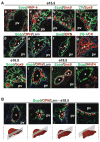
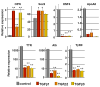
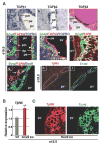
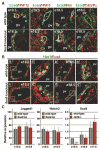
Results: Biliary tubulogenesis started with formation of asymmetrical ductal structures, lined on the portal side by cholangiocytes and on the parenchymal side by hepatoblasts. When the ducts grew from the hilum to the periphery, the hepatoblasts lining the asymmetrical structures differentiated to cholangiocytes, thereby allowing formation of symmetrical ducts lined only by cholangiocytes. We also provide evidence that transforming growth factor-beta promotes differentiation of the hepatoblasts lining the asymmetrical structures. In the absence of SOX9, the maturation of asymmetrical structures into symmetrical ducts was delayed. This was associated with abnormal expression of CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein alpha and Homolog of Hairy/Enhancer of Split-1, as well as of the transforming growth factor-beta receptor type II, which are regulators of biliary development.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that biliary development proceeds according to a new mode of tubulogenesis characterized by transient asymmetry and whose timing is controlled by SOX9.
Figures



References
-
- Kamath BM, Piccoli DA. Heritable disorders of the bile ducts. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2003;32:857–875. - PubMed
-
- Lemaigre F, Zaret KS. Liver development update: new embryo models, cell lineage control, and morphogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Zhao R, Duncan SA. Embryonic development of the liver. Hepatology. 2005;41:956–967. - PubMed
-
- Shiojiri N. The origin of intrahepatic bile duct cells in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984;79:25–39. - PubMed
-
- Van Eyken P, Sciot R, Callea F, et al. The development of the intrahepatic bile ducts in man: A keratin-immunohistochemical study. Hepatology. 1988;8:1586–1595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

