Novel recombinant virus assay for measuring susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtypes to clinically approved drugs
- PMID: 19403770
- PMCID: PMC2708496
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01739-08
Novel recombinant virus assay for measuring susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtypes to clinically approved drugs
Abstract
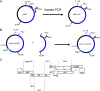
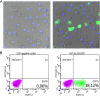
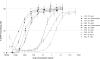
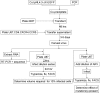
Combination therapy can successfully suppress human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication in patients but selects for drug resistance, requiring subsequent resistance-guided therapeutic changes. This report describes the development and validation of a novel assay that offers a uniform method to measure susceptibility to all clinically approved HIV type 1 (HIV-1) drugs targeting reverse transcriptase (RT), protease (PR), integrase (IN), and viral entry. It is an assay in which the antiviral effect on infection within a single replication cycle is measured in triply transfected U87.CD4.CXCR4.CCR5 cells, based on homologous recombination between patient-derived amplicons and molecular proviral clones tagged with the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter gene and from which certain viral genomic regions are removed. The deletions stretch from p17 codon 7 to PR codon 98 in pNL4.3-DeltagagPR-EGFP, from PR codons 1 to 99 in pNL4.3-DeltaPR-EGFP, from RT codons 1 to 560 in pNL4.3-DeltaRT-EGFP, from IN codons 1 to 288 in pNL4.3-DeltaIN-EGFP, and from gp120 codon 34 to gp41 codon 237 in pNL4.3-Deltaenv-EGFP. The optimized experimental conditions enable the investigation of patient samples regardless of viral subtype or coreceptor use. The extraction and amplification success rate for a set of clinical samples belonging to a broad range of HIV-1 group M genetic forms (A-J, CRF01-03, CRF05, and CRF12-13) and displaying a viral load range of 200 to >500,000 RNA copies/ml was 97%. The drug susceptibility measurements, based on discrimination between infected and noninfected cells on a single-cell level by flow cytometry, were reproducible, with coefficients of variation for resistance ranging from 7% to 31%, and were consistent with scientific literature in terms of magnitude and specificity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inclusion of full length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gag sequences in viral recombinants applied to drug susceptibility phenotyping.J Virol Methods. 2002 Jul;104(2):147-60. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(02)00059-9. J Virol Methods. 2002. PMID: 12088824
-
A new strategy based on recombinant viruses as a tool for assessing drug susceptibility of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Med Virol. 2007 Feb;79(2):127-37. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20770. J Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17177310
-
T-cell line for HIV drug screening using EGFP as a quantitative marker of HIV-1 replication.Biotechniques. 2006 Jan;40(1):91-100. doi: 10.2144/000112072. Biotechniques. 2006. PMID: 16454046
-
Genotypic testing for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drug resistance.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002 Apr;15(2):247-77. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.2.247-277.2002. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 11932232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotypic resistance tests for the management of the HIV-infected patient with non-B viral isolates.Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 2003;106:75-8. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 2003. PMID: 15000590 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of the highly conserved N-glycan at Asn260 of HIV-1 gp120 affects folding and lysosomal degradation of gp120, and results in loss of viral infectivity.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 26;9(6):e101181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101181. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24967714 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef inhibits Protease activity and its absence alters protein content of mature viral particles.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 18;9(4):e95352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095352. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24748174 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Next Generation Sequencing Sample Pre-Processing Bias in HIV-1 Complete Genome Sequencing.Viruses. 2016 Jan 7;8(1):12. doi: 10.3390/v8010012. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26751471 Free PMC article.
-
Novel method for simultaneous quantification of phenotypic resistance to maturation, protease, reverse transcriptase, and integrase HIV inhibitors based on 3'Gag(p2/p7/p1/p6)/PR/RT/INT-recombinant viruses: a useful tool in the multitarget era of antiretroviral therapy.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Aug;55(8):3729-42. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00396-11. Epub 2011 May 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21628544 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on recently developed assays for detection of resistance/sensitivity to reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Dec;102(23):9925-9936. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9390-x. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30269214 Review.
References
-
- Abecasis, A. B., K. Deforche, J. Snoeck, L. T. Bacheler, P. McKenna, A. P. Carvalho, P. Gomes, R. J. Camacho, and A. M. Vandamme. 2005. Protease mutation M89I/V is linked to therapy failure in patients infected with the HIV-1 non-B subtypes C, F or G. AIDS 191799-1806. - PubMed
-
- Abecasis, A. B., K. Deforche, L. T. Bacheler, P. McKenna, A. P. Carvalho, P. Gomes, A. M. Vandamme, and R. J. Camacho. 2006. Investigation of baseline susceptibility to protease inhibitors in HIV-1 subtypes C, F, G and CRF02_AG. Antivir. Ther. 11581-589. - PubMed
-
- Brenner, B., D. Turner, M. Oliveira, D. Moisi, M. Detorio, M. Carobene, R. G. Marlink, J. Schapiro, M. Roger, and M. A. Wainberg. 2003. A V106M mutation in HIV-1 clade C viruses exposed to efavirenz confers cross-resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. AIDS 17F1-F5. - PubMed
-
- Choe, S. S., E. Stawiski, and N. T. Parkin. 2007. Interpretation of drug susceptibility and replication capacity results from subtype C HIV-1 protease/RT is not influenced by the subtype of the resistance test vector, poster 1f07. Abstr. XV Int. HIV Drug Resistance Workshop 2007.
-
- Daelemans, D., C. Pannecoucque, G. N. Pavlakis, O. Tabarrini, and E. De Clercq. 2005. A novel and efficient approach to discriminate between pre- and post transcription inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 671574-1580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

