Early deficits in spatial memory and theta rhythm in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 19403808
- PMCID: PMC6665868
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4699-08.2009
Early deficits in spatial memory and theta rhythm in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
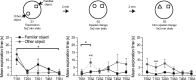
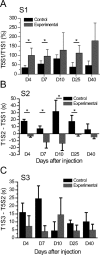
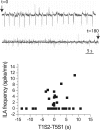
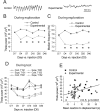
Patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), the most common form of epilepsy in adults, often display cognitive deficits. The time course and underlying mechanisms of cognitive decline remain unknown during epileptogenesis (the process leading to epilepsy). Using the rat pilocarpine model of TLE, we performed a longitudinal study to assess spatial and nonspatial cognitive performance during epileptogenesis. In parallel, we monitored interictal-like activity (ILA) in the hippocampal CA1 region, as well as theta oscillations, a brain rhythm central to numerous cognitive processes. Here, we report that spatial memory was altered soon after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus, i.e., already during the seizure-free, latent period. Spatial deficits correlated with a decrease in the power of theta oscillations but not with the frequency of ILA. Spatial deficits persisted when animals had spontaneous seizures (chronic stage) without further modification. In contrast, nonspatial memory performances remained unaffected throughout. We conclude that the reorganization of hippocampal circuitry that immediately follows the initial insult can affect theta oscillation mechanisms, in turn, resulting in deficits in hippocampus-dependent memory tasks. These deficits may be dissociated from the process that leads to epilepsy itself but could instead constitute, as ILA, early markers in at-risk patients and/or provide beneficial therapeutic targets.
Figures
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Hunt PR, Rawlins JN. The effects of hippocampal lesions upon spatial and non-spatial tests of working memory. Behav Brain Res. 1986;19:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Aldenkamp A, Arends J. The relative influence of epileptic EEG discharges, short nonconvulsive seizures, and type of epilepsy on cognitive function. Epilepsia. 2004;45:54–63. - PubMed
-
- Aldenkamp AP, Arends J, Overweg-Plandsoen TC, van Bronswijk KC, Schyns-Soeterboek A, Linden I, Diepman L. Acute cognitive effects of nonconvulsive difficult-to-detect epileptic seizures and epileptiform electroencephalographic discharges. J Child Neurol. 2001;16:119–123. - PubMed
-
- Aldenkamp AP, Arends J, Verspeek S, Berting M. The cognitive impact of epileptiform EEG-discharges; relationship with type of cognitive task. Child Neuropsychol. 2004;10:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Allen G, Barnard H, McColl R, Hester AL, Fields JA, Weiner MF, Ringe WK, Lipton AM, Brooker M, McDonald E, Rubin CD, Cullum CM. Reduced hippocampal functional connectivity in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:1482–1487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
