Beneficial endocrine but adverse exocrine effects of sitagliptin in the human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic rat model of type 2 diabetes: interactions with metformin
- PMID: 19403868
- PMCID: PMC2699878
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0058
Beneficial endocrine but adverse exocrine effects of sitagliptin in the human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic rat model of type 2 diabetes: interactions with metformin
Abstract
Objective: We sought to establish the extent and mechanisms by which sitagliptin and metformin singly and in combination modify islet disease progression in human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic (HIP) rats, a model for type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: HIP rats were treated with sitagliptin, metformin, sitagliptin plus metformin, or no drug as controls for 12 weeks. Fasting blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell mass, function, and turnover were measured in each group.
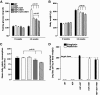
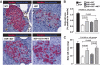
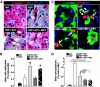
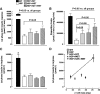
Results: Sitagliptin plus metformin had synergistic effects to preserve beta-cell mass in HIP rats. Metformin more than sitagliptin inhibited beta-cell apoptosis. Metformin enhanced hepatic insulin sensitivity; sitagliptin enhanced extrahepatic insulin sensitivity with a synergistic effect in combination. beta-Cell function was partially preserved by sitagliptin plus metformin. However, sitagliptin treatment was associated with increased pancreatic ductal turnover, ductal metaplasia, and, in one rat, pancreatitis.
Conclusions: The combination of metformin and sitagliptin had synergistic actions to preserve beta-cell mass and function and enhance insulin sensitivity in the HIP rat model of type 2 diabetes. However, adverse actions of sitagliptin treatment on exocrine pancreas raise concerns that require further evaluation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
One year of sitagliptin treatment protects against islet amyloid-associated β-cell loss and does not induce pancreatitis or pancreatic neoplasia in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Aug 15;305(4):E475-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00025.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23736544 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sitagliptin or metformin added to pioglitazone monotherapy in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.Metabolism. 2010 Jun;59(6):887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 20015525 Clinical Trial.
-
Sitagliptin with metformin: profile of a combination for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Oct;43(10):681-9. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.10.1136901. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17987221
-
Sitagliptin and metformin--novel combination therapy.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 Mar;12(4):641-6. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.556113. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 21291346 Review.
-
Sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a review of recent clinical trials.Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 Feb;24(2):489-96. doi: 10.1185/030079908x261069. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008. PMID: 18182122 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe acute pancreatitis in pregnancy.Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2015;2015:239068. doi: 10.1155/2015/239068. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 25628906 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal mTOR regulates GLP-1 production in mouse L cells.Diabetologia. 2015 Aug;58(8):1887-97. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3632-6. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 26037201
-
Incretin-based therapy and pancreatitis: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Apr;6(7):131. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.02.24. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29955591 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, pancreatic cancer and acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 15;8(1):782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19055-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29335646 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Expression in Normal and Neoplastic Human Pancreatic Tissues.Pancreas. 2016 Apr;45(4):613-9. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000521. Pancreas. 2016. PMID: 26495786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH: Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 1414– 1431 - PubMed
-
- Polonsky KS, Given BD, Hirsch LJ, Tillil H, Shapiro ET, Beebe C, Frank BH, Galloway JA, Van Cauter E: Abnormal patterns of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1231– 1239 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

