Intravaginal gene silencing using biodegradable polymer nanoparticles densely loaded with small-interfering RNA
- PMID: 19404239
- PMCID: PMC2693358
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat2444
Intravaginal gene silencing using biodegradable polymer nanoparticles densely loaded with small-interfering RNA
Abstract
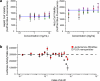
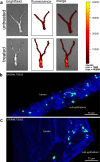
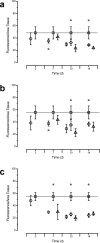
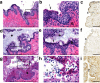
Vaginal instillation of small-interfering RNA (siRNA) using liposomes has led to silencing of endogenous genes in the genital tract and protection against challenge from infectious disease. Although siRNA lipoplexes are easily formulated, several of the most effective transfection agents available commercially may be toxic to the mucosal epithelia and none are able to provide controlled or sustained release. Here, we demonstrate an alternative approach using nanoparticles composed entirely of FDA-approved materials. To render these materials effective for gene silencing, we developed novel approaches to load them with high amounts of siRNA. A single dose of siRNA-loaded nanoparticles to the mouse female reproductive tract caused efficient and sustained gene silencing. Knockdown of gene expression was observed proximal (in the vaginal lumen) and distal (in the uterine horns) to the site of topical delivery. In addition, nanoparticles penetrated deep into the epithelial tissue. This is the first report demonstrating that biodegradable polymer nanoparticles are effective delivery vehicles for siRNA to the vaginal mucosa.
Figures



Comment in
-
Drug delivery: Old polymer learns new tracts.Nat Mater. 2009 Jun;8(6):447-8. doi: 10.1038/nmat2456. Nat Mater. 2009. PMID: 19458640 No abstract available.
References
-
- Veazey RS, et al. Protection of macaques from vaginal SHIV challenge by vaginally delivered inhibitors of virus-cell fusion. Nature. 2005;438:99–102. - PubMed
-
- Richardson JL, Illum L. Penetration enhancement for polypeptides through epithelia. D. Routes of delivery case studies. 8. The vaginal route of peptide and protein drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 1992;8:341–366.
-
- Veazey RS, et al. Prevention of virus transmission to macaque monkeys by a vaginally applied monoclonal antibody to HIV-1 gp120. Nat Med. 2003;9:343–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

