MAVS-mediated apoptosis and its inhibition by viral proteins
- PMID: 19404494
- PMCID: PMC2674933
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005466
MAVS-mediated apoptosis and its inhibition by viral proteins
Abstract
Background: Host responses to viral infection include both immune activation and programmed cell death. The mitochondrial antiviral signaling adaptor, MAVS (IPS-1, VISA or Cardif) is critical for host defenses to viral infection by inducing type-1 interferons (IFN-I), however its role in virus-induced apoptotic responses has not been elucidated.
Principal findings: We show that MAVS causes apoptosis independent of its function in initiating IFN-I production. MAVS-induced cell death requires mitochondrial localization, is caspase dependent, and displays hallmarks of apoptosis. Furthermore, MAVS(-/-) fibroblasts are resistant to Sendai virus-induced apoptosis. A functional screen identifies the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A and the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) nonstructural protein (NSP15) as inhibitors of MAVS-induced apoptosis, possibly as a method of immune evasion.
Significance: This study describes a novel role for MAVS in controlling viral infections through the induction of apoptosis, and identifies viral proteins which inhibit this host response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
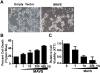
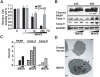


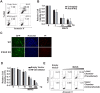
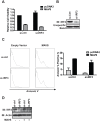


References
-
- Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell. 2005;122:669–682. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, Coban C, Kumar H, et al. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:981–988. - PubMed
-
- Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li LY, Zhai Z, et al. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol Cell. 2005;19:727–740. - PubMed
-
- Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2005;437:1167–1172. - PubMed
-
- Sun Q, Sun L, Liu HH, Chen X, Seth RB, et al. The specific and essential role of MAVS in antiviral innate immune responses. Immunity. 2006;24:633–642. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

