Induction of the expression of profibrotic cytokines and growth factors in normal human peripheral blood monocytes by gadolinium contrast agents
- PMID: 19404939
- PMCID: PMC2737360
- DOI: 10.1002/art.24471
Induction of the expression of profibrotic cytokines and growth factors in normal human peripheral blood monocytes by gadolinium contrast agents
Abstract
Objective: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) is a severe fibrosing disorder occurring in patients with renal insufficiency. The majority of patients with this disorder have documented exposure to magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents containing Gd. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid bismethylamide (Gd[DTPA-BMA]; Omniscan) as compared with Gd-DTPA and GdCl3 on the expression and production of cytokines and growth factors by normal human peripheral blood monocytes in vitro and to examine whether conditioned media from Gd-exposed peripheral blood monocytes could induce a profibrotic phenotype in dermal fibroblasts.
Methods: Normal human peripheral blood monocytes isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque gradient centrifugation and plastic adherence were incubated with various concentrations of Gd[DTPA-BMA], Gd-DTPA, or GdCl3. Gene expression of interleukins 4, 6, and 13, interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor alpha, transforming growth factor beta, connective tissue growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor were assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. Production and secretion of cytokines and growth factors by Gd compound-exposed monocytes was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay proteome multiplex arrays. The effects of conditioned media from the Gd compound-exposed monocytes on the phenotype of normal human dermal fibroblasts were examined by real-time PCR and Western blotting.
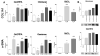
Results: The 3 Gd-containing compounds stimulated the expression and production of numerous cytokines and growth factors by normal human peripheral blood monocytes. Conditioned media from these cells induced a profibrotic phenotype in normal human dermal fibroblasts.
Conclusion: The 3 Gd-containing compounds studied induce potent cellular responses in normal human peripheral blood monocytes, which may participate in the development of tissue fibrosis in NSF.
Figures
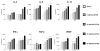

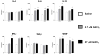
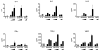

References
-
- Cowper SE, Robin HS, Steinberg SM, Su LD, Supta S, LeBoit PE. Scleromyxoedema-like cutaneous disease in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet. 2000;356:1000–1001. - PubMed
-
- Cowper SE, Su LD, Bhawan J, Robin HS, LeBoit PE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Mackay-Wiggan JM, Cohen DJ, Hardy MA, Knobler EH, Grossman ME. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (scleromyxedema-like illness of renal disease) J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Swartz RD, Crofford LJ, Phan SH, Ike RW, Su LD. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: a novel cutaneous fibrosing disorder in patients with renal failure. Am J Med. 2003;114:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez SA, Artlett CM, Sandorfi N, Derk C, Latinis K, Sawaya H, Haddad R, Shanahan JC. Dialysis-associated systemic fibrosis (nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy): study of inflammatory cells and transforming growth factor beta1 expression in affected skin. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2660–2666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

