Noninvasive, in vivo imaging of blood-oxygenation dynamics within the mouse brain using photoacoustic microscopy
- PMID: 19405708
- PMCID: PMC2676448
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3095799
Noninvasive, in vivo imaging of blood-oxygenation dynamics within the mouse brain using photoacoustic microscopy
Abstract
Photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) has been used to obtain high-resolution, noninvasive images of the in vivo mouse brain. In this work, we exploit the high-depth and temporal resolutions of PAM to noninvasively image the blood-oxygenation dynamics of multiple cortex vessels in the mouse brain simultaneously in response to controlled hypoxic and hyperoxic challenges. These results confirm the ability of PAM to track blood oxygenation in the mouse brain, a critical aspect of imaging brain activity through the hemodynamic response.
Figures
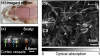
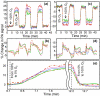
References
-
- Hafezparast M, Ahmad-Annuar A, Wood NW, Tabrizi SJ, Fisher EMC. Mouse models for neurological disease. The Lancet Neurology. 2002;1(4):215–224. - PubMed
-
- Xu MH, Wang LHV. Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2006;77(4)
-
- Zhang HF, Maslov K, Sivaramakrishnan M, Stoica G, Wang LHV. Imaging of hemoglobin oxygen saturation variations in single vessels in vivo using photoacoustic microscopy. Applied Physics Letters. 2007;90(5)
-
- Grinvald A, Lieke E, Frostig RD, Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN. Functional architecture of cortex revealed by optical imaging of intrinsic signals. Nature. 1986;324(6095):361–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

