Daptomycin in experimental murine pneumococcal meningitis
- PMID: 19405978
- PMCID: PMC2685802
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-50
Daptomycin in experimental murine pneumococcal meningitis
Abstract
Background: Daptomycin, a lipopeptide antibiotic, could be an alternative to vancomycin for treatment of pneumococcal meningitis. We determined the activity of daptomycin versus vancomycin, with dexamethasone as an adjuvant, in a murine model of pneumococcal meningitis.
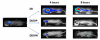
Methods: Ninety-six 25-30 gram mice were inoculated intracisternally with serotype 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae modified by the integration of a luminescent lux operon. All mice were treated with either dexamethasone 1 mg/kg intraperitoneally every 6 hours alone or in combination with either vancomycin or daptomycin, also administered intraperitoneally. Serum antimicrobial concentrations were selected to approximate those achieved in humans. Following treatment, bioluminescence and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bacterial concentrations were determined. Caspase-3 staining was used to assess apoptosis on brain histopathology.
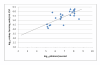
Results: Sixteen hours post intracisternal inoculation, bacterial titers in CSF were 6.8 log10 cfu/ml. Amongst the animals given no antibiotic, vancomycin 50 mg/kg at 16 and 20 hours or daptomycin 25 mg/kg at 16 hours, CSF titers were 7.6, 3.4, and 3.9 log10 cfu/ml, respectively, at 24 hours post infection (p-value, < 0.001 for both vancomycin or daptomycin versus no antibiotic); there was no significant difference in bactericidal activity between the vancomycin and daptomycin groups (p-value, 0.18). CSF bioluminescence correlated with bacterial titer (Pearson regression coefficient, 0.75). The amount of apoptosis of brain parenchymal cells was equivalent among treatment groups.
Conclusion: Daptomycin or vancomycin, when given in combination with dexamethasone, is active in the treatment of experimental pneumococcal meningitis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of dexamethasone on the efficacy of daptomycin in the therapy of experimental pneumococcal meningitis.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015 Jul;46(1):28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.01.014. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015. PMID: 25813395
-
Daptomycin is highly efficacious against penicillin-resistant and penicillin- and quinolone-resistant pneumococci in experimental meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Oct;48(10):3928-33. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.10.3928-3933.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15388454 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of brain injury by the nonbacteriolytic antibiotic daptomycin in experimental pneumococcal meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun;51(6):2173-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01014-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17371820 Free PMC article.
-
Management of pneumococcal meningitis.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002 Jun;21(6):589-91; discussion 613-4. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200206000-00034. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002. PMID: 12182395 Review.
-
New therapies for pneumococcal meningitis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004 Apr;13(4):393-401. doi: 10.1517/13543784.13.4.393. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15102588 Review.
Cited by
-
Daptomycin versus vancomycin in treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus meningitis in an experimental rabbit model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Mar;57(3):1556-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01996-12. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23318792 Free PMC article.
-
Anidulafungin treatment of candidal central nervous system infection in a murine model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Aug;53(8):3576-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00646-09. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19506064 Free PMC article.
-
Bright fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions.J Bacteriol. 2015 Mar;197(5):807-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.02221-14. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25512311 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effect of non-bacteriolytic antibiotic and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases prevents brain injury and preserves learning, memory and hearing function in experimental paediatric pneumococcal meningitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 21;15(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1272-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30131074 Free PMC article.
-
In-vivo monitoring of infectious diseases in living animals using bioluminescence imaging.Virulence. 2018 Jan 1;9(1):28-63. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1371897. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 28960132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

