Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 mediates denbinobin-induced apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 19405983
- PMCID: PMC2686692
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-43
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 mediates denbinobin-induced apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells
Abstract
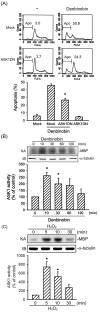
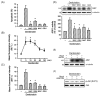
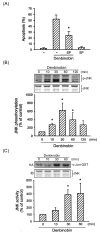
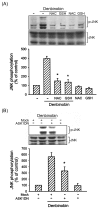
In the present study, we explore the role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) in denbinobin-induced apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma (A549) cells. Denbinobin-induced cell apoptosis was attenuated by an ASK1 dominant-negative mutant (ASK1DN), two antioxidants (N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and glutathione (GSH)), a c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor (SP600125), and an activator protein-1 (AP-1) inhibitor (curcumin). Treatment of A549 cells with denbinobin caused increases in ASK1 activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and these effects were inhibited by NAC and GSH. Stimulation of A549 cells with denbinobin caused JNK activation; this effect was markedly inhibited by NAC, GSH, and ASK1DN. Denbinobin induced c-Jun phosphorylation, the formation of an AP-1-specific DNA-protein complex, and Bim expression. Bim knockdown using a bim short interfering RNA strategy also reduced denbinobin-induced A549 cell apoptosis. The denbinobin-mediated increases in c-Jun phosphorylation and Bim expression were inhibited by NAC, GSH, SP600125, ASK1DN, JNK1DN, and JNK2DN. These results suggest that denbinobin might activate ASK1 through ROS production to cause JNK/AP-1 activation, which in turn induces Bim expression, and ultimately results in A549 cell apoptosis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Denbinobin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells via Akt inactivation, Bad activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction.Toxicol Lett. 2008 Feb 28;177(1):48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.12.009. Epub 2007 Dec 28. Toxicol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18262737
-
Thrombin-induced connective tissue growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts requires the ASK1/JNK/AP-1 pathway.J Immunol. 2009 Jun 15;182(12):7916-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801582. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19494316
-
Connective tissue growth factor induces collagen I expression in human lung fibroblasts through the Rac1/MLK3/JNK/AP-1 pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):2823-2833. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23906792
-
Role of Bim in diallyl trisulfide-induced cytotoxicity in human cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Jan;112(1):118-27. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22896. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21053278 Free PMC article.
-
[Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Signaling: Regulatory Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Roles].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(10):1235-1241. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.19-00141. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 31582606 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Bufalin enhances the antitumor effect of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer.Oncol Lett. 2012 Oct;4(4):792-798. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.783. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23205102 Free PMC article.
-
Quinonoids: Therapeutic Potential for Lung Cancer Treatment.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 6;2020:2460565. doi: 10.1155/2020/2460565. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32337232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous glutathione contributes to cisplatin resistance in lung cancer A549 cells.Am J Transl Res. 2018 May 15;10(5):1295-1309. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29887946 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta-dependent and -independent roles of STRAP in cancer.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(1):105-15. doi: 10.2741/3678. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ASK1 inhibits proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells via inactivating TAZ.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2785-2799. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042617 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

