A dual mechanism of cytoprotection afforded by M-LDH in embryonic heart H9C2 cells
- PMID: 19406174
- PMCID: PMC2719797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.04.007
A dual mechanism of cytoprotection afforded by M-LDH in embryonic heart H9C2 cells
Abstract
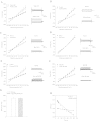
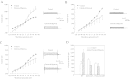
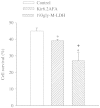
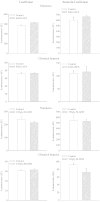
Muscle form of lactate dehydrogenase (M-LDH), a minor LDH form in cardiomyocytes, physically interacts with ATP-sensitive K+ (K ATP) channel-forming subunits. Here, we have shown that expression of 193gly-M-LDH, an inactive mutant of M-LDH, inhibit regulation of the K ATP channels activity by LDH substrates in embryonic rat heart H9C2 cells. In cells expressing 193gly-M-LDH chemical hypoxia has failed to activate K ATP channels. The similar results were obtained in H9C2 cells expressing Kir6.2AFA, a mutant form of Kir6.2 with largely decreased K+ conductance. Kir6.2AFA has slightly, but significantly, reduced cellular survival under chemical hypoxia while the deleterious effect of 193gly-M-LDH was significantly more pronounced. The levels of total and subsarcolemmal ATP in H9C2 cells were not affected by Kir6.2AFA, but the expression of 193gly-M-LDH led to lower levels of subsarcolemmal ATP during chemical hypoxia. We conclude that M-LDH regulates both the channel activity and the levels of subsarcolemmal ATP and that both mechanism contribute to the M-LDH-mediated cytoprotection.
Figures
References
-
- Zingman L.V., Alekseev A.E., Hodgson-Zingman D., Terzic A. , ATP-sensitive K+ channels: metabolic sensing and cardioprotection. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007;103:1888–1893. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki N., Gonoi T., Clement J.P., Wang C.Z., Aguilar-Bryan L., Bryan J., Seino S. A family of sulfonylurea receptors determines the pharmacological properties of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Neuron. 1996;16:1011–1017. - PubMed
-
- Carrasco A.J., Dzeja P.P., Alekseev A.E., Pucar D., Zingman L.V., Abraham M.R., Hodgson D., Bienengraeber M., Puceat M., Janssen E., Wieringa B., Terzic A. Adenylate kinase phosphotransfer communicates cellular energetic signals to ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001;98:7623–7628. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S18744/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 059528/Z/99/Z/JMW/CP/JF/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0400608(71317)/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400608/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/02/091/14227/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

