Nonrecovery of kidney function and death after acute on chronic renal failure
- PMID: 19406959
- PMCID: PMC2676192
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05571008
Nonrecovery of kidney function and death after acute on chronic renal failure
Abstract
Background and objectives: Relatively little is known about clinical outcomes, especially long-term outcomes, among patients who have chronic kidney disease (CKD) and experience superimposed acute renal failure (ARF; acute on chronic renal failure).
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We tracked 39,805 members of an integrated health care delivery system in northern California who were hospitalized during 1996 through 2003 and had prehospitalization estimated GFR (eGFR) <45 ml/min per 1.73 m(2). Superimposed ARF was defined as having both a peak inpatient serum creatinine greater than the last outpatient serum creatinine by > or =50% and receipt of acute dialysis.
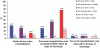
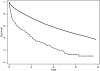
Results: Overall, 26% of CKD patients who suffered superimposed ARF died during the index hospitalization. There was a high risk for developing ESRD within 30 d of hospital discharge that varied with preadmission renal function, being 42% among hospital survivors with baseline eGFR 30-44 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) and 63% among hospital survivors with baseline eGFR 15-29 ml/min per 1.73 m(2). Compared with patients who had CKD and did not experience superimposed ARF, those who did had a 30% higher long-term risk for death or ESRD.
Conclusions: In a large, community-based cohort of patients with CKD, an episode of superimposed dialysis-requiring ARF was associated with very high risk for nonrecovery of renal function. Dialysis-requiring ARF also seemed to be an independent risk factor for long-term risk for death or ESRD.
Figures
References
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW, Hogg RJ, Perrone RD, Lau J, Eknoyan G: National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med 139: 137–147, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT: Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: A prospective study. Am J Med 74: 243–248, 1983 - PubMed
-
- Leblanc M, Kellum JA, Gibney RT, Lieberthal W, Tumlin J, Mehta R: Risk factors for acute renal failure: Inherent and modifiable risks. Curr Opin Crit Care 11: 533–536, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

