Estimating glomerular filtration rate: Cockcroft-Gault and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formulas compared to renal inulin clearance
- PMID: 19406960
- PMCID: PMC2676189
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05371008
Estimating glomerular filtration rate: Cockcroft-Gault and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formulas compared to renal inulin clearance
Abstract
Background and objectives: Evaluation of renal function by estimation of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is very important for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). The Cockcroft-Gault (CG) and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formulas are the most commonly used estimations.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Estimated GFR values by each formula were compared with measured GFR (mGFR) by renal inulin clearance in 2208 European adults (46% women, 1.4% Caribbean blacks), with and without CKD, and mean mGFR 72.4 +/- 39.0 (range 2.2 to 177.2) ml/min/1.73 m(2).
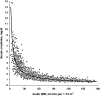
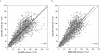
Results: Overall, the CG and MDRD formulas showed bias (mean difference) -3.5 ml/min/1.73 m(2) (5.3%), P < 0.001, and -9.8 ml/min/1.73 m(2) (-6.4%), P < 0.001; precision (SD of bias) 21.5 ml/min/1.73 m(2) (43.1%) and 20.0 ml/min/1.73 m(2) (33.0%); limits of agreement (2 SD by Bland-Altman method) 39.5 to -46.5 (range 86.0) ml/min/1.73 m(2) and 30.2 to -49.8 (range 80.0) ml/min/1.73 m(2); and accuracy within +/-30% of mGFR 70.8 and 69.0%, respectively. Both formulas showed a trend for decreasing accuracy with lower mGFR levels. According to the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI)-CKD classification's five GFR groups, the CG and MDRD formulas properly assigned 61.6 and 57.1% of the entire population and had a range of positive predictive values 42.6 to 81.8% and 39.6 to 85.2% and of negative predictive values 81.7 to 96.6% and 76.4 to 97.5%, respectively.
Conclusions: The CG and MDRD formulas had some limitations for proper GFR estimation and K/DOQI-CKD classification by GFR levels alone.
Figures

Comment in
-
eGFR: Readjusting its rating.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 May;4(5):867-9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01830309. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19414566 No abstract available.
References
-
- Smith HW: The reliability of inulin as a measure of glomerular filtration. In: The Kidney: Structure and Function in Health and Disease, New York, Oxford University Press, pp 231-238, 1951
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39[Suppl 1]: S1–S266, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Levey AS: Measurement of renal function in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int 38: 167–184, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Gaspari F, Perico N, Remuzzi G: Application of newer clearance techniques for the determination of glomerular filtration rate. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 7: 675–680, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Kemperman FA, Krediet RT, Arisz L: Formula-derived prediction of the glomerular filtration rate from plasma creatinine concentration. Nephron 91: 547–558, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

