Oxidized LDL modulates apoptosis of regulatory T cells in patients with ESRD
- PMID: 19406979
- PMCID: PMC2689899
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008070734
Oxidized LDL modulates apoptosis of regulatory T cells in patients with ESRD
Retraction in
-
Notice of retractions.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Mar;25(3):645. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014010004. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24459234 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
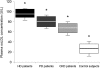
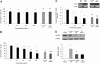
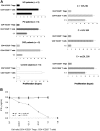
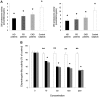
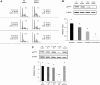
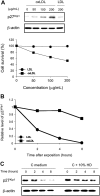
Increased levels of oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL) contribute to the increased risk for atherosclerosis, which persists even after adjusting for traditional risk factors, among patients with ESRD. Regulatory T cells (CD4+/CD25+ Tregs), which down-regulate T cell responses to foreign and self-antigens, are protective in murine atherogenesis, but whether similar immunoregulation occurs in humans with ESRD is unknown. Because cellular defense systems against oxLDL involve proteolytic degradation, the authors investigated the role of oxLDL on proteasome activity of CD4+/CD25+ Tregs in patients with ESRD. CD4+/CD25+ Tregs isolated from uremic patients' peripheral blood, especially that of chronically hemodialyzed patients, failed to suppress cell proliferation, exhibited cell-cycle arrest, and entered apoptosis by altering proteasome activity. Treating CD4+/CD25+ Tregs with oxLDL or uremic serum ex vivo decreased the number and suppressive capacity of CD4+/CD25+ Tregs. In vitro, oxLDL promoted the accumulation of p27Kip1, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor responsible for G1 cell cycle arrest, and increased apoptosis in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. In summary, proteasome inhibition by oxLDL leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, dramatically affecting the number and suppressive capacity of CD4+/CD25+ Tregs in chronically hemodialyzed patients. This response may contribute to the immune dysfunction, microinflammation, and atherogenesis observed in patients with ESRD.
Figures
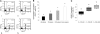
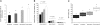

References
-
- Cheung AK, Sarnak MJ, Yan G, Dwyer JT, Heyka RJ, Rocco MV, Teehan BP, Levey AS: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risks in chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 58: 353–362, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Longenecker JC, Coresh J, Powe NR, Levey AS, Fink NE, Martin A, Klag MJ: Traditional cardiovascular disease risk factors in dialysis patients compared with the general population: The CHOICE Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1918–1927, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420: 868–874, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Binder CJ, Chang MK, Shaw PX, Miller YI, Hartvigsen K, Dewan A, Witztum JL: Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat Med 8: 1218–1226, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Vaziri ND: Dyslipidemia of chronic renal failure: The nature, mechanisms, and potential consequences. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F262–F272, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

