NK-cell-mediated killing of target cells triggers robust antigen-specific T-cell-mediated and humoral responses
- PMID: 19406986
- PMCID: PMC2710917
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-201467
NK-cell-mediated killing of target cells triggers robust antigen-specific T-cell-mediated and humoral responses
Abstract
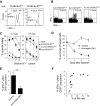
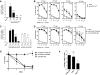
Previous work showed that administration of antigen-expressing apoptotic cells in vivo results in antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses independent of Toll-like receptor signaling. We report here that natural killer (NK) cells can serve a function directly upstream of this pathway and initiate robust adaptive immune responses via killing of antigen-expressing target cells. This pathway is highly sensitive, in that administration of as few as 10(4) target cells induced detectable antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses. Importantly, NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity of target cells could also induce robust antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell responses, which were critical for subsequent CD8+ T-cell priming and IgG responses. Unlike adaptive immune responses induced by gamma-irradiated cells, the NK-cell pathway required myeloid differentiating factor 88 (MyD88) and Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-beta (Trif) signaling. NK cells have previously been shown to detect and kill pathogen-infected host cells, as well as neoplastic cells and tissue allografts. The present data provide further evidence that they also discharge a strong tie with their relatives in the adaptive immune system. We think that the recognition and killing of target cells by NK cells represents an important pathway for the generation of robust CD8+ T and humoral responses that may be exploited for vaccine development.
Figures




References
-
- Blankenstein T. The role of inflammation in tumour growth and tumour suppression. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;256:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Gallucci S, Lolkema M, Matzinger P. Natural adjuvants: endogenous activators of dendritic cells. Nat Med. 1999;5:1249–1255. - PubMed
-
- Degli-Esposti MA, Smyth MJ. Close encounters of different kinds: dendritic cells and NK cells take centre stage. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:112–124. - PubMed
-
- Kelly JM, Darcy PK, Markby JL, et al. Induction of tumor-specific T cell memory by NK cell-mediated tumor rejection. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

