Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins
- PMID: 19407142
- PMCID: PMC2827199
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1173041
Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins
Abstract
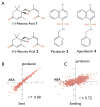
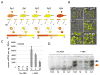
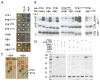
Type 2C protein phosphatases (PP2Cs) are vitally involved in abscisic acid (ABA) signaling. Here, we show that a synthetic growth inhibitor called pyrabactin functions as a selective ABA agonist. Pyrabactin acts through PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE 1 (PYR1), the founding member of a family of START proteins called PYR/PYLs, which are necessary for both pyrabactin and ABA signaling in vivo. We show that ABA binds to PYR1, which in turn binds to and inhibits PP2Cs. We conclude that PYR/PYLs are ABA receptors functioning at the apex of a negative regulatory pathway that controls ABA signaling by inhibiting PP2Cs. Our results illustrate the power of the chemical genetic approach for sidestepping genetic redundancy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Plant biology. Stressed out over a stress hormone.Science. 2009 May 22;324(5930):1012-3. doi: 10.1126/science.324_1012. Science. 2009. PMID: 19460982 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yoshida R, et al. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002;43:1473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

