Structure of the human Nac1 POZ domain
- PMID: 19407373
- PMCID: PMC2675581
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109012214
Structure of the human Nac1 POZ domain
Abstract
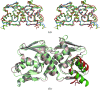
Nac1 is a POZ-domain transcription factor that is involved in the self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. It is overexpressed in ovarian serous carcinoma and targeting the interactions of its POZ domain is a potential therapeutic strategy. Nac1 lacks a zinc-finger DNA-binding domain and thereby differs from most other POZ-domain transcription factors. Here, the crystal structure of the Nac1 POZ domain at 2.1 A resolution is reported. The Nac1 POZ domain crystallized as a dimer in which the interaction interfaces between subunits resemble those found in the POZ-zinc finger transcription factors. The organization of the Nac1 POZ-domain core resembles reported POZ-domain structures, whereas the C-terminus differs markedly. The C-terminal alpha-helix of the Nac1 POZ domain is shorter than that observed in most other POZ-domain transcription factors; variation in the organization of this region may be a general feature of POZ-domain structures.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, K. F., Melnick, A., Lax, S., Bouchard, D., Liu, J., Kiang, C. L., Mayer, S., Takahashi, S., Licht, J. D. & Privé, G. G. (2003). Mol. Cell, 12, 1551–1564. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 760–763. - PubMed
-
- Davidson, B., Berner, A., Trope, C. G., Wang, T. L. & Shih, I.-M. (2007). Hum. Pathol. 38, 1030–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

