The spatio-temporal mapping of epileptic networks: combination of EEG-fMRI and EEG source imaging
- PMID: 19408351
- PMCID: PMC2977852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.01.070
The spatio-temporal mapping of epileptic networks: combination of EEG-fMRI and EEG source imaging
Abstract
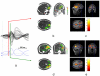
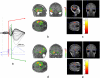
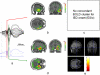
Simultaneous EEG-fMRI acquisitions in patients with epilepsy often reveal distributed patterns of Blood Oxygen Level Dependant (BOLD) change correlated with epileptiform discharges. We investigated if electrical source imaging (ESI) performed on the interictal epileptiform discharges (IED) acquired during fMRI acquisition could be used to study the dynamics of the networks identified by the BOLD effect, thereby avoiding the limitations of combining results from separate recordings. Nine selected patients (13 IED types identified) with focal epilepsy underwent EEG-fMRI. Statistical analysis was performed using SPM5 to create BOLD maps. ESI was performed on the IED recorded during fMRI acquisition using a realistic head model (SMAC) and a distributed linear inverse solution (LAURA). ESI could not be performed in one case. In 10/12 remaining studies, ESI at IED onset (ESIo) was anatomically close to one BOLD cluster. Interestingly, ESIo was closest to the positive BOLD cluster with maximal statistical significance in only 4/12 cases and closest to negative BOLD responses in 4/12 cases. Very small BOLD clusters could also have clinical relevance in some cases. ESI at later time frame (ESIp) showed propagation to remote sources co-localised with other BOLD clusters in half of cases. In concordant cases, the distance between maxima of ESI and the closest EEG-fMRI cluster was less than 33 mm, in agreement with previous studies. We conclude that simultaneous ESI and EEG-fMRI analysis may be able to distinguish areas of BOLD response related to initiation of IED from propagation areas. This combination provides new opportunities for investigating epileptic networks.
Figures
References
-
- Aghakhani Y., Bagshaw A.P. fMRI activation during spike and wave discharges in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Brain. 2004;127(Pt 5):1127–1144. - PubMed
-
- Al-Asmi A., Benar C.G. fMRI activation in continuous and spike-triggered EEG–fMRI studies of epileptic spikes. Epilepsia. 2003;44(10):1328–1339. - PubMed
-
- Allen P.J., Polizzi G. Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: the problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. NeuroImage. 1998;8(3):229–239. - PubMed
-
- Allen P.J., Josephs O. A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. NeuroImage. 2000;12(2):230–239. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J., Friston K. Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning—a unified framework. NeuroImage. 1997;6(3):209–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
