White Tea extract induces lipolytic activity and inhibits adipogenesis in human subcutaneous (pre)-adipocytes
- PMID: 19409077
- PMCID: PMC2685800
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-6-20
White Tea extract induces lipolytic activity and inhibits adipogenesis in human subcutaneous (pre)-adipocytes
Abstract
Background: The dramatic increase in obesity-related diseases emphasizes the need to elucidate the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying fat metabolism. To investigate how natural substances influence lipolysis and adipogenesis, we determined the effects of White Tea extract on cultured human subcutaneous preadipocytes and adipocytes.
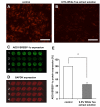
Methods: For our in vitro studies we used a White Tea extract solution that contained polyphenols and methylxanthines. Utilizing cultured human preadipocytes we investigated White Tea extract solution-induced inhibition of triglyceride incorporation during adipogenesis and possible effects on cell viability. In vitro studies on human adipocytes were performed aiming to elucidate the efficacy of White Tea extract solution to stimulate lipolytic activity. To characterize White Tea extract solution-mediated effects on a molecular level, we analyzed gene expression of essential adipogenesis-related transcription factors by qRT-PCR and determined the expression of the transcription factor ADD1/SREBP-1c on the protein level utilizing immunofluorescence analysis.
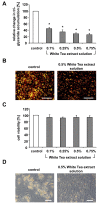
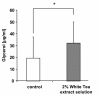
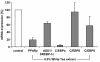
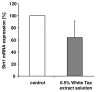
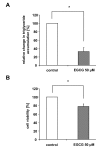
Results: Our data show that incubation of preadipocytes with White Tea extract solution significantly decreased triglyceride incorporation during adipogenesis in a dose-dependent manner (n = 10) without affecting cell viability (n = 10). These effects were, at least in part, mediated by EGCG (n = 10, 50 μM). In addition, White Tea extract solution also stimulated lipolytic activity in adipocytes (n = 7). Differentiating preadipocytes cultivated in the presence of 0.5% White Tea extract solution showed a decrease in PPARγ, ADD1/SREBP-1c, C/EBPα and C/EBPδ mRNA levels. Moreover, the expression of the transcription factor ADD1/SREBP-1c was not only decreased on the mRNA but also on the protein level.
Conclusion: White Tea extract is a natural source that effectively inhibits adipogenesis and stimulates lipolysis-activity. Therefore, it can be utilized to modulate different levels of the adipocyte life cycle.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

