Ultrasensitive prostate specific antigen assay following laparoscopic radical prostatectomy--an outcome measure for defining the learning curve
- PMID: 19409146
- PMCID: PMC2758435
- DOI: 10.1308/003588409X428289
Ultrasensitive prostate specific antigen assay following laparoscopic radical prostatectomy--an outcome measure for defining the learning curve
Abstract
Introduction: Radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP) performed laparoscopically is a popular treatment with curative intent for organ-confined prostate cancer. After surgery, prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels drop to low levels which can be measured with ultrasensitive assays. This has been described in the literature for open RRP but not for laparoscopic RRP. This paper describes PSA changes in the first 300 consecutive patients undergoing non-robotic laparoscopic RRP by a single surgeon.
Objectives: To use ultrasensitive PSA (uPSA) assays to measure a PSA nadir in patients having laparoscopic radical prostatectomy below levels recorded by standard assays. The aim was to use uPSA nadir at 3 months' post-prostatectomy as an early surrogate end-point of oncological outcome. In so doing, laparoscopic oncological outcomes could then be compared with published results from other open radical prostatectomy series with similar end-points. Furthermore, this end-point could be used in the assessment of the surgeon's learning curve.
Patients and methods: Prospective, comprehensive, demographic, clinical, biochemical and operative data were collected from all patients undergoing non-robotic laparoscopic RRP. We present data from the first 300 consecutive patients undergoing laparoscopic RRP by a single surgeon. uPSA was measured every 3 months post surgery.
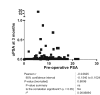
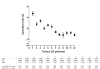
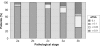
Results: Median follow-up was 29 months (minimum 3 months). The likelihood of reaching a uPSA of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months is 73% for the first 100 patients. This is statistically lower when compared with 83% (P < 0.05) for the second 100 patients and 80% for the third 100 patients (P < 0.05). Overall, 84% of patients with pT2 disease and 66% patients with pT3 disease had a uPSA of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months. Pre-operative PSA, PSA density and Gleason score were not correlated with outcome as determined by a uPSA of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months. Positive margins correlate with outcome as determined by a uPSA of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months but operative time and tumour volume do not (P < 0.05). Attempt at nerve sparing had no adverse effect on achieving a uPSA of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months.
Conclusions: uPSA can be used as an early end-point in the analysis of oncological outcomes after radical prostatectomy. It is one of many measures that can be used in calculating a surgeon's learning curve for laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and in bench-marking performance. With experience, a surgeon can achieve in excess of an 80% chance of obtaining a uPSA nadir of < or = 0.01 ng/ml at 3 months after laparoscopic RRP for a British population. This is equivalent to most published open series.
Figures

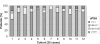

References
-
- Eastham JA, Scardino PT. Radical prostatectomy. In: Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan EDJ, Wein AJ, editors. Campbell's Urology. 7th edn. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1998. pp. 2547–64.
-
- Tooher R, Swindle P, Woo H, Miller J, Maddern G. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer: a systematic review of comparative studies. J Urol. 2006;175:2011–7. - PubMed
-
- Hasan WA, Gill IS. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: current status. BJU Int. 2004;94:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Vickers AJ, Bianco FJ, Serio AM, Eastham JA, Schrag D, et al. The surgical learning curve for prostate cancer control after radical prostatectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1171–7. - PubMed
-
- Wright TP. Factors affecting the cost of airplanes. J Aeronaut Sci. 1936;3:122–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

