Synaptic and extrasynaptic factors governing glutamatergic retinal waves
- PMID: 19409268
- PMCID: PMC2807181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.015
Synaptic and extrasynaptic factors governing glutamatergic retinal waves
Abstract
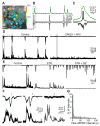
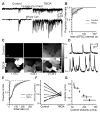
In the few days prior to eye-opening in mice, the excitatory drive underlying waves switches from cholinergic to glutamatergic. Here, we describe the unique synaptic and spatiotemporal properties of waves generated by the retina's glutamatergic circuits. First, knockout mice lacking vesicular glutamate transporter type 1 do not have glutamatergic waves, but continue to exhibit cholinergic waves, demonstrating that the two wave-generating circuits are linked. Second, simultaneous outside-out patch and whole-cell recordings reveal that retinal waves are accompanied by transient increases in extrasynaptic glutamate, directly demonstrating the existence of glutamate spillover during waves. Third, the initiation rate and propagation speed of retinal waves, as assayed by calcium imaging, are sensitive to pharmacological manipulations of spillover and inhibition, demonstrating a role for both signaling pathways in shaping the spatiotemporal properties of glutamatergic retinal waves.
Figures






References
-
- Allen TG. The ‘sniffer-patch’ technique for detection of neurotransmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Bansal A, Singer JH, Hwang BJ, Xu W, Beaudet A, Feller MB. Mice lacking specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits exhibit dramatically altered spontaneous activity patterns and reveal a limited role for retinal waves in forming ON and OFF circuits in the inner retina. J Neurosci. 2000;20:7672–7681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, Khalilov I, Represa A, Gozlan H. Interneurons set the tune of developing networks. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:422–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

