State-dependent variability of neuronal responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation of the visual cortex
- PMID: 19409273
- PMCID: PMC2953477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.012
State-dependent variability of neuronal responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation of the visual cortex
Abstract
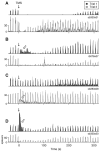
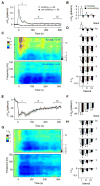
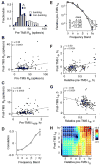
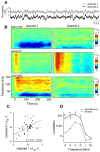
Electrical brain stimulation is a promising tool for both experimental and clinical applications. However, the effects of stimulation on neuronal activity are highly variable and poorly understood. To investigate the basis of this variability, we performed extracellular recordings in the visual cortex following application of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Our measurements of spiking and local field potential activity exhibit two types of response patterns which are characterized by the presence or absence of spontaneous discharge following stimulation. This variability can be partially explained by state-dependent effects, in which higher pre-TMS activity predicts larger post-TMS responses. These results reveal the possibility that variability in the neural response to TMS can be exploited to optimize the effects of stimulation. It is conceivable that this feature could be utilized in real time during the treatment of clinical disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Allen EA, Pasley BN, Duong T, Freeman RD. Transcranial magnetic stimulation elicits coupled neural and hemodynamic consequences. Science. 2007;317:1918–1921. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini A, de Noordhout AM, Sandor PS, Schoenen J. Electrophysiological studies in migraine: a comprehensive review of their interest and limitations. Cephalalgia. 2003;23 1:13–31. - PubMed
-
- Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;1:1106–1107. - PubMed
-
- Berardelli A, Inghilleri M, Rothwell JC, Romeo S, Curra A, Gilio F, Modugno N, Manfredi M. Facilitation of muscle evoked responses after repetitive cortical stimulation in man. Exp Brain Res. 1998;122:79–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

