Sleep deprivation attenuates inflammatory responses and ischemic cell death
- PMID: 19409382
- PMCID: PMC2696570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.04.018
Sleep deprivation attenuates inflammatory responses and ischemic cell death
Abstract
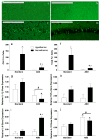
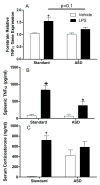
Although the biological function of sleep remains uncertain, the consequences of sleep deprivation are well-described and are reported to be detrimental to cognitive function and affective well-being. Sleep deprivation also is strongly associated with elevated risk factors for cardiovascular disease. We used a mouse model of cardiac arrest/cardiopulmonary resuscitation to test the hypothesis that acute sleep deprivation would exacerbate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration after global ischemia. The resulting data led to a rejection of our hypothesis that sleep deprivation is necessarily detrimental. Indeed, acute sleep deprivation (ASD) was associated with a reduction in ischemia-induced interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) gene expression and attenuation of neuronal damage in the hippocampus. Further, sleep deprivation increased gene expression of two anti-inflammatory cytokines, IL-6 and IL-10 that are associated with improved ischemic outcome. To determine whether the anti-inflammatory properties of ASD were specific to ischemia, mice were treated systemically with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a potent inflammogen. Acute sleep deprivation attenuated the central and peripheral increase in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and increased IL-10 expression. Together, the ischemia and LPS data suggest that, ASD produces an anti-inflammatory bias that could be exploited to improve medical procedures that are compromised by inflammation.
Figures




References
-
- Arumugam TV, Gleichmann M, Tang SC, Mattson MP. Hormesis/preconditioning mechanisms, the nervous system and aging. Ageing Research Reviews. 2006;5:165–178. - PubMed
-
- Barber PA, Hach S, Tippett LJ, Ross L, Merry AF, Milsom P. Cerebral ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging are associated with neurocognitive decline after cardiac surgery. Stroke. 2008;39:1427–1433. - PubMed
-
- Bliwise DL. Sleep in normal aging and dementia. Sleep. 1993;16:40–81. - PubMed
-
- DeVries AC, Craft TK, Glasper ER, Neigh GN, Alexander JK. 2006 Curt P. Richter award winner: Social influences on stress responses and health. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2007;32:587–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

