Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 19411070
- PMCID: PMC2881229
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.016
Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion
Abstract
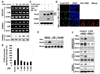
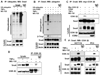
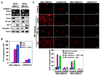
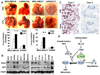
The increased motility and invasiveness of tumor cells are reminiscent of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which occurs during embryonic development, wound healing, and metastasis. In this study, we found that Snail is stabilized by the inflammatory cytokine TNFalpha through the activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. We demonstrated that NF-kappaB is required for the induction of COP9 signalosome 2 (CSN2), which, in turn, blocks the ubiquitination and degradation of Snail. Furthermore, we showed that the expression of Snail correlated with the activation of NF-kappaB in cancer cell lines and metastatic tumor samples. Knockdown of Snail expression inhibited cell migration and invasion induced by inflammatory cytokines and suppressed inflammation-mediated breast cancer metastasis. Our study provides a plausible mechanism for inflammation-induced metastasis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Inflamed snail speeds metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2009 May 5;15(5):355-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.04.003. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19411063
References
-
- Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Berse M, Bounpheng M, Huang X, Christy B, Pollmann C, Dubiel W. Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Id1 and Id3 is mediated by the COP9 signalosome. J Mol Biol. 2004;343:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Blanco MJ, Moreno-Bueno G, Sarrio D, Locascio A, Cano A, Palacios J, Nieto MA. Correlation of Snail expression with histological grade and lymph node status in breast carcinomas. Oncogene. 2002;21:3241–3246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

