The role of B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 19411764
- PMCID: PMC2673851
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38010
The role of B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
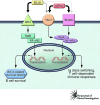
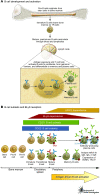
SLE, a chronic, multisystem autoimmune disorder with a broad range of symptoms, involves defective B cell selection and elimination of self-reactive B cells. B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS), a soluble ligand of the TNF cytokine family, is a prominent factor in B cell differentiation, homeostasis, and selection. BLyS levels affect survival signals and selective apoptosis of autoantibody-producing B cells. High levels of BLyS may relax B cell selection and contribute to autoantibody production, exacerbating the SLE disease state. This review discusses the mechanism of BLyS action on B cells, its role in SLE, and specific targeting of BLyS in the treatment of SLE.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

