A primate-specific, brain isoform of KCNH2 affects cortical physiology, cognition, neuronal repolarization and risk of schizophrenia
- PMID: 19412172
- PMCID: PMC2756110
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1962
A primate-specific, brain isoform of KCNH2 affects cortical physiology, cognition, neuronal repolarization and risk of schizophrenia
Abstract
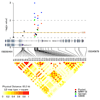
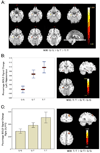
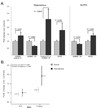
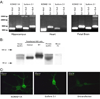
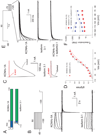
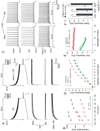
Organized neuronal firing is crucial for cortical processing and is disrupted in schizophrenia. Using rapid amplification of 5' complementary DNA ends in human brain, we identified a primate-specific isoform (3.1) of the ether-a-go-go-related K(+) channel KCNH2 that modulates neuronal firing. KCNH2-3.1 messenger RNA levels are comparable to full-length KCNH2 (1A) levels in brain but three orders of magnitude lower in heart. In hippocampus from individuals with schizophrenia, KCNH2-3.1 expression is 2.5-fold greater than KCNH2-1A expression. A meta-analysis of five clinical data sets (367 families, 1,158 unrelated cases and 1,704 controls) shows association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in KCNH2 with schizophrenia. Risk-associated alleles predict lower intelligence quotient scores and speed of cognitive processing, altered memory-linked functional magnetic resonance imaging signals and increased KCNH2-3.1 mRNA levels in postmortem hippocampus. KCNH2-3.1 lacks a domain that is crucial for slow channel deactivation. Overexpression of KCNH2-3.1 in primary cortical neurons induces a rapidly deactivating K(+) current and a high-frequency, nonadapting firing pattern. These results identify a previously undescribed KCNH2 channel isoform involved in cortical physiology, cognition and psychosis, providing a potential new therapeutic drug target.
Figures
Comment in
-
Breaking the gene barrier in schizophrenia.Nat Med. 2009 May;15(5):488-90. doi: 10.1038/nm0509-488. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19424205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ioannidis JP, Ntzani EE, Trikalinos TA, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG. Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat Genet. 2001;29:306–309. - PubMed
-
- Trikalinos TA, Ntzani EE, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Ioannidis JP. Establishment of genetic associations for complex diseases is independent of early study findings. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12:762–769. - PubMed
-
- Weiss KM, Terwilliger JD. How many diseases does it take to map a gene with SNPs? Nat Genet. 2000;26:151–157. - PubMed
-
- Grarup N, et al. Studies of association of variants near the HHEX, CDKN2A/B, and IGF2BP2 genes with type 2 diabetes and impaired insulin release in 10,705 Danish subjects: validation and extension of genome-wide association studies. Diabetes. 2007;56:3105–3111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

