Molecular and biochemical pharmacology of the histamine H4 receptor
- PMID: 19413568
- PMCID: PMC2697796
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00250.x
Molecular and biochemical pharmacology of the histamine H4 receptor
Abstract
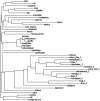
The elucidation of the human genome has had a major impact on histamine receptor research. The identification of the human H4 receptor by several groups has been instrumental for a new appreciation of the role of histamine in the modulation of immune function. In this review, we summarize the historical developments and the molecular and biochemical pharmacology of the H4 receptor.
Figures




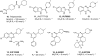
References
-
- Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Schwartz JC. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class H3 of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983;302:832–837. - PubMed
-
- Bakker RA, Lozada AF, van Marle A, Shenton FC, Drutel G, Karlstedt K, et al. Discovery of naturally occurring splice variants of the rat histamine H3 receptor that act as dominant-negative isoforms. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69:1194–1206. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Barnard R, Barnard A, Salmon G, Liu W, Sreckovic S. Histamine-induced actin polymerization in human eosinophils: an imaging approach for histamine H4 receptor. Cytometry. 2008;73:299–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

