Stiffening effect of cholesterol on disordered lipid phases: a combined neutron spin echo + dynamic light scattering analysis of the bending elasticity of large unilamellar vesicles
- PMID: 19413968
- PMCID: PMC2711415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.01.045
Stiffening effect of cholesterol on disordered lipid phases: a combined neutron spin echo + dynamic light scattering analysis of the bending elasticity of large unilamellar vesicles
Abstract
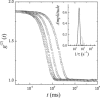
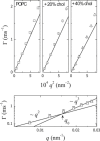
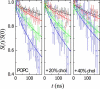
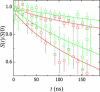
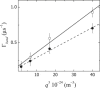
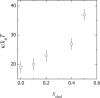
In this study, the center-of-mass diffusion and shape fluctuations of large unilamellar 1-palmitoyl-2-oleyl-sn-glycero-phosphatidylcholine vesicles prepared by extrusion are studied by means of neutron spin echo in combination with dynamic light scattering. The intermediate scattering functions were measured for several different values of the momentum transfer, q, and for different cholesterol contents in the membrane. The combined analysis of neutron spin echo and dynamic light scattering data allows calculation of the bending elastic constant, kappa, of the vesicle bilayer. A stiffening effect monitored as an increase of kappa with increasing cholesterol molar ratio is demonstrated by these measurements.
Figures
References
-
- Presti F.T. The role of cholesterol in membrane fluidity. In: Aloia R.C., Boggs J.M., editors. Membrane Fluidity in Biology, vol 4. Academic Press; New York: 1985. pp. 97–146.
-
- Finegold L.X. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 1993. Cholesterol in Membrane Models.
-
- Mouritsen O.G., Jørgensen K. Dynamical order and disorder in lipid bilayers. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 1994;73:3–25. - PubMed
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J. 5th ed. Taylor & Francis; New York & London: 2008. Molecular Biology of the Cell.
-
- Jamieson G.A., Robinson D.M. Butterworths; London: 1977. Mammalian Cell Membranes vol 2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

