The role of cardiolipin in the structural organization of mitochondrial membranes
- PMID: 19413994
- PMCID: PMC2757492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.04.019
The role of cardiolipin in the structural organization of mitochondrial membranes
Abstract
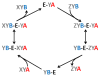
Considerable progress has recently been made in understanding the role of cardiolipin in mitochondria. In this brief review, we discuss new data that show how cardiolipin specifically contributes to the lateral organization of mitochondrial membranes. We argue that the function of cardiolipin has to be understood in the context of dynamic membrane assembly rather than static membrane structure, and we propose that remodeling of cardiolipin, i.e. the formation of uniformly substituted molecular species, may reduce the energy barrier of the assembly process.
Figures
References
-
- Jiang F, Rizavi HS, Greenberg ML. Cardiolipin is not essential for the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on fermentable and non-fermentable carbon sources. Mol Microbiol. 1997;26:481–491. - PubMed
-
- Jiang F, Ryan MT, Schlame M, Zhao M, Gu Z, Klingenberg M, Pfanner N, Greenberg ML. Absence of cardiolipin in crd1 null mutant results in decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and reduced mitochondrial function. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:22387–22394. - PubMed
-
- Schlame M, Rua D, Greenberg ML. The biosynthesis and functional role of cardiolipin. Progr Lipid Res. 2000;39:257–288. - PubMed
-
- Palsdottir H, Lojero CG, Trumpower BL, Hunte C. Structure of the yeast bc1 complex with a hydroxyquinone anion QO site inhibitor bound. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:31303–31311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

