Survival of aged nursing home residents with hip fracture
- PMID: 19414511
- PMCID: PMC2844133
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glp019
Survival of aged nursing home residents with hip fracture
Abstract
Background: Little is known about mortality in nursing home residents with hip fracture. This study examined the effect of pre-fracture characteristics, hospital complications, and post-fracture complications on mortality in residents with hip fracture.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of 195 long-term care residents (153 women, 42 men) with hip fracture (1999-2006) followed for mortality until June 30, 2007. Pre-fracture characteristics (age, sex, cognition, functional status, comorbidities, body mass index), hospital complications (acute myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, delirium, infection) and 6-month complications (delirium, pneumonia, pressure ulcer, urinary tract infection [UTI]) were evaluated as potential predictors of mortality.
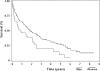
Results: During a median follow-up of 1.4 years, 150 participants (76.9%) died. Male residents were nearly twice as likely to die compared with female residents (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.9, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.2-3.0). Other pre-fracture characteristics associated with increased mortality included older age (HR per 5 years = 1.3, 95% CI 1.1-1.6), low functional status (HR = 1.7, 95% CI 1.0-3.0), anemia (HR = 1.6, 95% CI 1.1-2.5), and coronary artery disease (HR = 2.0, 95% CI 1.3-2.9). Mortality was 70% greater among residents with a pressure ulcer or pneumonia within 6 months of hip fracture (pressure ulcer, HR = 1.7, 95% CI 1.2-2.6; pneumonia, HR = 1.7, 95% CI 1.1-2.7). Individual hospital complications and post-fracture delirium and UTI were not significant predictors of mortality.
Conclusions: In addition to pre-fracture characteristics, potentially modifiable post-fracture complications including pressure ulcer and pneumonia were associated with increased mortality in nursing home residents with hip fracture. Prevention strategies to reduce pressure ulcers and pneumonia may help reduce mortality in this frail population.
Figures
References
-
- Ooms ME, Vlasman P, Lips P, Nauta J, Bouter LM, Valkenburg HA. The incidence of hip fractures in independent and institutionalized elderly people. Osteoporos Int. 1994;4(1):6–10. - PubMed
-
- Rudman IW, Rudman D. High rate of fractures for men in nursing homes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1989;68(1):2–5. - PubMed
-
- Hannan EL, Magaziner J, Wang JJ, et al. Mortality and locomotion 6 months after hospitalization for hip fracture: risk factors and risk-adjusted hospital outcomes. JAMA. 2001;285(21):2736–2742. - PubMed
-
- Jiang HX, Majumdar SR, Dick DA, et al. Development and initial validation of a risk score for predicting in-hospital and 1-year mortality in patients with hip fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(3):494–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical