Genome-wide analysis of survival in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19414679
- PMCID: PMC2690391
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7906
Genome-wide analysis of survival in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Lung cancer, of which 85% is non-small-cell (NSCLC), is the leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. We used genome-wide analysis of tumor tissue to investigate whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in tumors are prognostic factors in early-stage NSCLC.
Patients and methods: One hundred early-stage NSCLC patients from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) were used as a discovery set and 89 NSCLC patients collected by the National Institute of Occupational Health, Norway, were used as a validation set. DNA was extracted from flash-frozen lung tissue with at least 70% tumor cellularity. Genome-wide genotyping was done using the high-density SNP chip. Copy numbers were inferred using median smoothing after intensity normalization. Cox models were used to screen and validate significant SNPs associated with the overall survival.
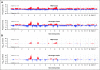
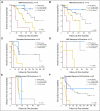
Results: Copy number gains in chromosomes 3q, 5p, and 8q were observed in both MGH and Norwegian cohorts. The top 50 SNPs associated with overall survival in the MGH cohort (P < or = 2.5 x 10(-4)) were selected and examined using the Norwegian cohort. Five of the top 50 SNPs were validated in the Norwegian cohort with false discovery rate lower than 0.05 (P < .016) and all five were located in known genes: STK39, PCDH7, A2BP1, and EYA2. The numbers of risk alleles of the five SNPs showed a cumulative effect on overall survival (P(trend) = 3.80 x 10(-12) and 2.48 x 10(-7) for MGH and Norwegian cohorts, respectively).
Conclusion: Five SNPs were identified that may be prognostic of overall survival in early-stage NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman PC, Mauer AM, Vokes EE. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2000;355:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Hung RJ, McKay JD, Gaborieau V, et al. A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25. Nature. 2008;452:633–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

