De novo deletion 17p13.1 chronic lymphocytic leukemia shows significant clinical heterogeneity: the M. D. Anderson and Mayo Clinic experience
- PMID: 19414856
- PMCID: PMC4916942
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-210591
De novo deletion 17p13.1 chronic lymphocytic leukemia shows significant clinical heterogeneity: the M. D. Anderson and Mayo Clinic experience
Abstract
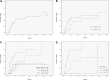
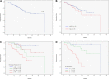
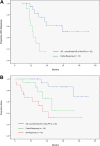
To determine the clinical fate of patients with de novo deletion 17p13.1 (17p-) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), we retrospectively studied the outcome of 99 treatment-naive 17p- CLL patients from the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center (n = 64) and the Mayo Clinic (n = 35). Among 67 asymptomatic patients followed for progression, 53% developed CLL requiring treatment over 3 years. Patients who had not progressed by 18 months subsequently had stable disease, with 3 of 19 patients progressing after follow-up of up to 70 months. Risk factors for progressive disease were Rai stage of 1 or higher and unmutated immunoglobulin variable region heavy chain (IgVH). The overall survival rate was 65% at 3 years. Rai stage 1 or higher, unmutated IgVH, and 17p- in 25% or more of nuclei were adverse factors for survival. The 3-year survival rates of patients with 1 or fewer, 2, and 3 of these factors were 95%, 74%, and 22%, respectively (P < .001). Response rates to therapy with rituximab (n = 6); purine analogues and rituximab (n = 25); and purine analogues, rituximab, and alemtuzumab (n = 16) combinations were 50%, 72%, and 81%, respectively. Patients with 17p- CLL exhibit clinical heterogeneity, with some patients experiencing an indolent course. Survival can be predicted using clinical and biologic characteristics.
Figures
References
-
- Geisler CH, Philip P, Christensen BE, et al. In B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia chromosome 17 abnormalities and not trisomy 12 are the single most important cytogenetic abnormalities for the prognosis: a cytogenetic and immunophenotypic study of 480 unselected newly diagnosed patients. Leuk Res. 1997;21:1011–1023. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1910–1916. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Fischer K, Bentz M, et al. p53 gene deletion predicts for poor survival and non-response to therapy with purine analogs in chronic B-cell leukemias. Blood. 1995;85:1580–1589. - PubMed
-
- Byrd JC, Smith L, Hackbarth ML, et al. Interphase cytogenetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia may predict response to rituximab. Cancer Res. 2003;63:36–38. - PubMed
-
- Stilgenbauer S, Krober A, Busch R, et al. 17p Deletion predicts for inferior overall survival after fludarabine-based first line therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: first analysis of genetics in the CLL4 Trial of the GCLLSG [abstract]. Blood. 2005;106 Abstract 715.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

