Flg22 regulates the release of an ethylene response factor substrate from MAP kinase 6 in Arabidopsis thaliana via ethylene signaling
- PMID: 19416906
- PMCID: PMC2683104
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810206106
Flg22 regulates the release of an ethylene response factor substrate from MAP kinase 6 in Arabidopsis thaliana via ethylene signaling
Abstract
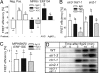
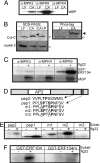
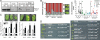
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-mediated responses are in part regulated by the repertoire of MAPK substrates, which is still poorly elucidated in plants. Here, the in vivo enzyme-substrate interaction of the Arabidopsis thaliana MAP kinase, MPK6, with an ethylene response factor (ERF104) is shown by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The interaction was rapidly lost in response to flagellin-derived flg22 peptide. This complex disruption requires not only MPK6 activity, which also affects ERF104 stability via phosphorylation, but also ethylene signaling. The latter points to a novel role of ethylene in substrate release, presumably allowing the liberated ERF104 to access target genes. Microarray data show enrichment of GCC motifs in the promoters of ERF104-up-regulated genes, many of which are stress related. ERF104 is a vital regulator of basal immunity, as altered expression in both erf104 and overexpressors led to more growth inhibition by flg22 and enhanced susceptibility to a non-adapted bacterial pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

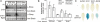
Comment in
-
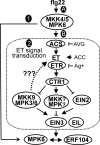
Sometimes new results raise new questions: the question marks between mitogen-activated protein kinase and ethylene signaling.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Jul;4(7):672-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810206106. Epub 2009 Jul 19. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19820303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakagami H, Pitzschke A, Hirt H. Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signalling. Trends Plants Sci. 2005;10:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Asai T, et al. MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature. 2002;415:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Ichimura K, et al. MEKK1 is required for MPK4 activation and regulates tissue-specific and temperature-dependent cell death in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:36969–36976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

