Steroid receptor coactivator-1 is necessary for regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone by chronic stress and glucocorticoids
- PMID: 19416907
- PMCID: PMC2683087
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812062106
Steroid receptor coactivator-1 is necessary for regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone by chronic stress and glucocorticoids
Abstract
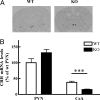
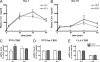
Adaptation to stress in vertebrates occurs via activation of hormonal and neuronal signaling cascades in which corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) plays a central role. Expression of brain CRH is subject to strong, brain-region specific regulation by glucocorticoid hormones and neurogenic intracellular signals. We hypothesized that Steroid Receptor Coactivator 1 (SRC-1), a transcriptional coregulator of the glucocorticoid receptor, is involved in the sensitivity of CRH regulation by stress-related factors. In the brains of SRC-1 knockout mice we found basal CRH mRNA levels to be lower in the central nucleus of the amygdala. Hypothalamic CRH up-regulation after chronic (but not acute) stress, as well as region-dependent up- and down-regulation induced by synthetic glucocorticoids, were significantly attenuated compared with wild type. The impaired induction of the crh gene by neurogenic signals was corroborated in AtT-20 cells, where siRNA and overexpression experiments showed that SRC-1 is necessary for full induction of a CRH promoter reporter gene by forskolin, suggestive of involvement of transcription factor CREB. In conclusion, SRC-1 is involved in positive and negative regulation of the crh gene, and an important factor for the adaptive capacity of stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
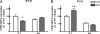
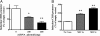
References
-
- Gray TS. Amygdaloid CRF pathways. Role in autonomic, neuroendocrine, and behavioral responses to stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;697:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Heinrichs SC, Koob GF. Corticotropin-releasing factor in brain: A role in activation, arousal, and affect regulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:427–440. - PubMed
-
- Herman JP, et al. Central mechanisms of stress integration: Hierarchical circuitry controlling hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical responsiveness. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003;24:151–180. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: Role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–557. - PubMed
-
- de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F. Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:463–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

