The organic cation transporter-3 is a pivotal modulator of neurodegeneration in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway
- PMID: 19416912
- PMCID: PMC2683105
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0900358106
The organic cation transporter-3 is a pivotal modulator of neurodegeneration in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway
Abstract
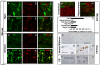
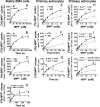
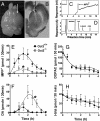
Toxic organic cations can damage nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathways as seen in most parkinsonian syndromes and in some cases of illicit drug exposure. Here, we show that the organic cation transporter 3 (Oct3) is expressed in nondopaminergic cells adjacent to both the soma and terminals of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. We hypothesized that Oct3 contributes to the dopaminergic damage by bidirectionally regulating the local bioavailability of toxic species. Consistent with this view, Oct3 deletion and pharmacological inhibition hampers the release of the toxic organic cation 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium from astrocytes and protects against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Furthermore, Oct3 deletion impairs the removal of the excess extracellular dopamine induced by methamphetamine and enhances striatal dopaminergic terminal damage caused by this psychostimulant. These results may have far-reaching implications for our understanding of the mechanism of cell death in a wide range of neurodegenerative diseases and may open new avenues for neuroprotective intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson's disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 2003;39:889–909. - PubMed
-
- Miller GW, Gainetdinov RR, Levey AI, Caron MG. Dopamine transporters and neuronal injury. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999;20:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Custer SK, et al. Bergmann glia expression of polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 produces neurodegeneration by impairing glutamate transport. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1302–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 ES07026/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS38370-09/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ES014899/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- AG021617/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS062180/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES01247/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007026/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS062180/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ES014899-02S1/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS042269/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES001247/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA022413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES014899/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS0641912/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042269/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

